Rook SDK
This SDK enables apps to extract and upload data from Apple Health and Health Connect. With this SDK, you will be able to extract and upload data. For more information, check out our demo app.
Installation
To build a project using ROOK in React Native, you need to use at least React v18 and React Native v70.
- The minimum version of Android SDK is 26, the target SDK is 34, and the Kotlin version is >= 1.8.10.**
- The SDK requires Xcode 16.0 or higher. To run your app using the ROOK SDK on a connected device with iOS 16.2 or later.
- The minimum version of iOS is 13.0.
npm
npm i react-native-rook-sdk
yarn
yarn add react-native-rook-sdk
Configuration
Add your client uuid in order to be authorized, follow the next example, add at the top level of your tree components the RookSyncGate, password refers to the secret key.
import { RookSyncGate } from "react-native-rook-sdk";
<RookSyncGate
environment="sandbox | production"
clientUUID="YOUR_CLIENT_UUID"
password="YOUR_PASSWORD"
enableLogs={true | false | undefined}
enableBackgroundSync={true | false}
enableEventsBackgroundSync={true | false | undefined}
>
<YOUR_COMPONENTS />
</RookSyncGate>;
The value of enableLogs will display or not local logs in the console for certain SDK operations. We recommend you to ask your users if they want to enable the automatic sync, then save their preference in local
storage and set enableBackgroundSync conditionally.
The value of enableEventsBackgroundSync will include or exclude the events of the background sync.
iOS Configuration
Then we need to add Apple Health Kit Framework to our project in order to that please:
- Open your project in Xcode.
- Click on your project file in the Project Navigator.
- Select your target and then click on the "Build Phases" tab.
- Click on the "+" button under the "Link Binary With Libraries" section and select "HealthKit.framework" from the list.
- Select your target and then click on the "Signing Capabilities" tab.
- Click on "Add Capability" and search for "HealthKit"
Additionally add the following to the info.plist
<key>NSHealthShareUsageDescription</key>
<string>This app requires access to your health and fitness data in order to track your workouts and activity levels.</string>
<key>NSHealthUpdateUsageDescription</key>
<string>This app requires permission to write healt data to HealthKit.</string>
Android Configuration
Then we need to configure the android project. open the android project inside android studio. We need to modify the AndroidManifest.xml file in order to access to the Health connection records.
We need to add inside your activity tag an intent filter to open Health Connect APP and your AndroidManifest.xml file should look like this
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
...
<application
...>
<activity
...>
<intent-filter>
...
</intent-filter>
<!-- For supported versions through Android 13, create an activity to show the rationale
of Health Connect permissions once users click the privacy policy link. -->
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="androidx.health.ACTION_SHOW_PERMISSIONS_RATIONALE" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<!-- For versions starting Android 14, create an activity alias to show the rationale
of Health Connect permissions once users click the privacy policy link. -->
<activity-alias
android:name="ViewPermissionUsageActivity"
android:exported="true"
android:permission="android.permission.START_VIEW_PERMISSION_USAGE"
android:targetActivity=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW_PERMISSION_USAGE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.HEALTH_PERMISSIONS" />
</intent-filter>
</activity-alias>
</application>
</manifest>
Included permissions for Android
This SDK will use the following permissions, there is no need to declare them in your manifest as the rook-sdk already declares them in its own manifest.
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACTIVITY_RECOGNITION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_HEALTH"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.POST_NOTIFICATIONS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_SLEEP"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_STEPS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_DISTANCE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_FLOORS_CLIMBED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_ELEVATION_GAINED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_OXYGEN_SATURATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_VO2_MAX"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_TOTAL_CALORIES_BURNED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_ACTIVE_CALORIES_BURNED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_HEART_RATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_RESTING_HEART_RATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_HEART_RATE_VARIABILITY"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_EXERCISE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_SPEED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_WEIGHT"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_HEIGHT"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_BLOOD_GLUCOSE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_BLOOD_PRESSURE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_HYDRATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_BODY_TEMPERATURE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_RESPIRATORY_RATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_NUTRITION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_MENSTRUATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_POWER"/>
Google may require you to provide an explanation about the FOREGROUND_SERVICE/FOREGROUND_SERVICE_HEALTH permissions,
these permissions are used by our Automatic Sync and Background Steps features, to extract health data and upload it to
ROOK servers. We recommend you to ask users for permission before enabling these features (Google may also require a
video proof of a screen where a user can turn on/off these features).
Request data access for Android
When you are developing with the Health Connect SDK, data access is unrestricted. To have data access when your app is launched on the Play Store, you must complete the Play Console Health apps declaration. More information can be found here.
You will se a list like below of the permissions your app uses, you will need to provide a description on how your app uses the data of each permission.
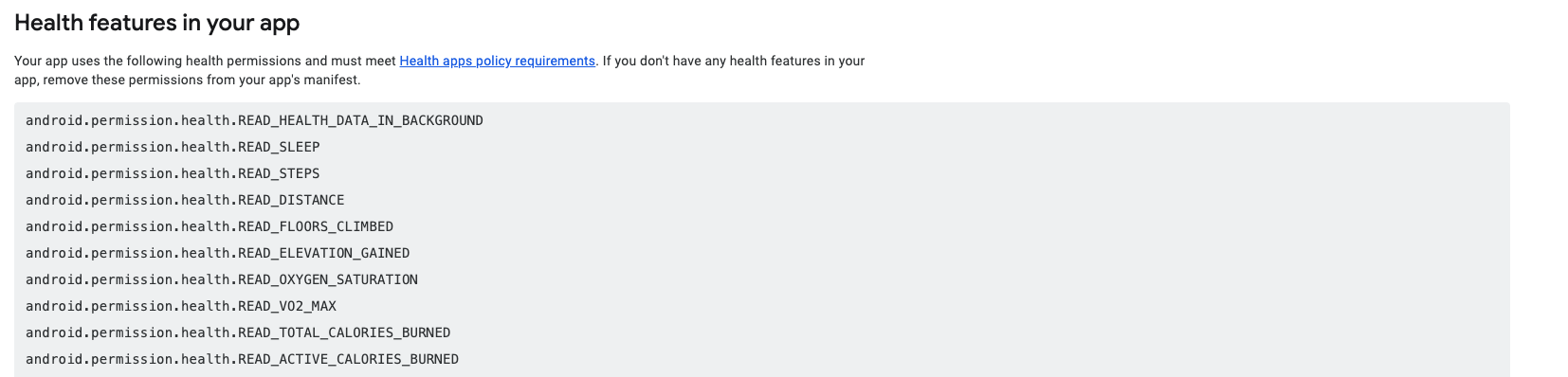
If you don't want access to a particular data type of Health Connect you can remove it.
Obfuscation for Android
If you are using obfuscation consider the following:
In your proguard-rules.pro add the following rule:
-keep class com.google.crypto.** { *; }
In your gradle.properties (Project level) add the following to disable R8 full mode:
android.enableR8.fullMode=false
If you want to enable full mode add the following rules to proguard-rules.pro:
# Keep generic signature of Call, Response (R8 full mode strips signatures from non-kept items).
-keep,allowobfuscation,allowshrinking interface retrofit2.Call
-keep,allowobfuscation,allowshrinking class retrofit2.Response
# With R8 full mode generic signatures are stripped for classes that are not
# kept. Suspend functions are wrapped in continuations where the type argument
# is used.
-keep,allowobfuscation,allowshrinking class kotlin.coroutines.Continuation
# Crypto
-keep class com.google.crypto.** { *; }
Usage
useRookConfiguration
The useRookConfiguration hook provides comprehensive configuration management for the ROOK SDK, offering methods to manage user settings, synchronization, and data sources across iOS and Android platforms.
import { useRookConfiguration } from 'react-native-rook-sdk'
const useRookConfiguration = () => {
ready: boolean;
getUserID: () => Promise<string>;
updateUserID: (userID: string) => Promise<boolean>;
clearUserID: (sources: SDKDataSource[]) => Promise<boolean>;
syncUserTimeZone: () => Promise<boolean>;
removeUserFromRook: (sources: SDKDataSource[]) => Promise<boolean>;
enableAppleHealthSync: () => Promise<boolean>;
disableAppleHealthSync: () => Promise<boolean>;
isAppleHealthSyncEnabled: () => Promise<boolean>;
scheduleAndroidYesterdaySync: () => Promise<boolean>;
enableSamsungSync: () => Promise<boolean>;
disableSamsungSync: () => Promise<boolean>;
isSamsungSyncEnabled: () => Promise<boolean>;}
Properties
ready: Boolean indicating whether the ROOK SDK is initialized and ready to accept method calls
User Management Functions
getUserID(): Retrieves the current user ID from the SDKupdateUserID(userID: string): Updates the user ID in the SDK and contextclearUserID(sources: SDKDataSource[]): Clears the current user ID from the SDK and specified data sourcesremoveUserFromRook(sources: SDKDataSource[]): Completely removes the user from ROOK services (requires recreating user and permissions afterward)
Synchronization Functions
syncUserTimeZone(): Synchronizes the user's current timezone with the ROOK SDK
Apple Health Sync Functions (iOS Only)
enableAppleHealthSync(): Enables automatic upload of summaries from the previous day when app opensdisableAppleHealthSync(): Disables automatic upload of summariesisAppleHealthSyncEnabled(): Checks if Apple Health sync is currently enabled
Android Background Sync Functions
scheduleAndroidYesterdaySync()- Schedules background sync for summaries and events data from previous day (supports Android 14 and earlier)
Samsung Health Functions (Android Only)
enableSamsungSync(): Enables Samsung Health data synchronizationdisableSamsungSync(): Disables Samsung Health data synchronizationisSamsungSyncEnabled(): Checks if Samsung Health sync is currently enabled Note: If you delete the user from the ROOK services you have to create the user again withupdateUserIDand request permissions.
Any call to updateUserID the userID will override the previous userID and reset the sync status, so if you are using background sync all health data will synchronize again the next time the app is launched.
useRookPermissions
This hook will help you to request permissions to extract data.
export type CheckPermissionsParam = {
type: PermissionsType;
};
export type PermissionsType =
| "appleExerciseTime"
| "appleMoveTime"
| "appleStandTime"
| "basalEnergyBurned"
| "activeEnergyBurned"
| "stepCount"
| "distanceCycling"
| "distanceWalkingRunning"
| "distanceSwimming"
| "swimmingStrokeCount"
| "flightsClimbed"
| "walkingSpeed"
| "walkingStepLength"
| "runningPower"
| "runningSpeed"
| "height"
| "bodyMass"
| "bodyMassIndex"
| "waistCircumference"
| "bodyFatPercentage"
| "bodyTemperature"
| "basalBodyTemperature"
| "appleSleepingWristTemperature"
| "heartRate"
| "restingHeartRate"
| "walkingHeartRateAverage"
| "heartRateVariabilitySDNN"
| "electrocardiogram"
| "workout"
| "sleepAnalysis"
| "sleepApneaEvent"
| "vo2Max"
| "oxygenSaturation"
| "respiratoryRate"
| "uvExposure"
| "biologicalSex"
| "dateOfBirth"
| "bloodPressureSystolic"
| "bloodPressureDiastolic"
| "bloodGlucose"
| "dietaryEnergyConsumed"
| "dietaryProtein"
| "dietarySugar"
| "dietaryFatTotal"
| "dietaryCarbohydrates"
| "dietaryFiber"
| "dietarySodium"
| "dietaryCholesterol";
const useRookPermissions: () => {
ready: boolean;
checkAvailability: () => Promise<CheckAvailabilityResponse>;
checkSamsungAvailability: () => Promise<CheckAvailabilityResponse>;
checkBackgroundReadStatus: () => Promise<BackgroundStatus>;
appleHealthHasPermissions: (
param?: CheckPermissionsParam
) => Promise<PermissionStatus>;
healthConnectHasPermissions: () => Promise<boolean>;
healthConnectHasPartialPermissions: () => Promise<boolean>;
samsungHealthHasPermissions: () => Promise<boolean>;
samsungHealthHasPartialPermissions: () => Promise<boolean>;
androidHasBackgroundPermissions: () => Promise<boolean>;
shouldRequestAndroidBackgroundPermissions: () => Promise<boolean>;
requestAllPermissions: () => Promise<RequestStatusPermissions>;
requestAllAppleHealthPermissions: () => Promise<RequestStatusPermissions>;
requestAllHealthConnectPermissions: () => Promise<RequestStatusPermissions>;
requestAppleHealthPermissions: (
permissions: PermissionsType[]
) => Promise<boolean>;
requestSamsungHealthPermissions: (
permissions?: SamsungHealthPermission[]
) => Promise<RequestStatusPermissions>;
requestAndroidBackgroundPermissions: () => Promise<RequestStatusPermissions>;
openAppleHealthSettings: () => Promise<void>;
openHealthConnectSettings: () => Promise<void>;
};
Properties
ready: Boolean indicating whether the ROOK SDK is initialized and ready to accept method calls
Availability Check Functions
checkAvailability(): Checks the availability of health services (Health Connect on Android, always returns 'INSTALLED' on iOS)- Returns:
Promise<CheckAvailabilityResponse> ('INSTALLED' | 'NOT_INSTALLED' | 'DISABLED' | 'NOT_READY' | 'OUTDATED' | 'NOT_SUPPORTED')
- Returns:
checkSamsungAvailability(): Checks the availability of Samsung Health services- Platform: Android only
- Returns:
Promise<CheckAvailabilityResponse>
checkBackgroundReadStatus(): Checks the background read status for Health Connect- Platform: Android only
- Returns:
Promise<BackgroundStatus> ('UNAVAILABLE' | 'PERMISSION_NOT_GRANTED' | 'PERMISSION_GRANTED')
Permission Check Functions
-
appleHealthHasPermissions(param?: CheckPermissionsParam): Checks if the app has Apple Health permissions for a specific data types- Platform: iOS only
- Parameters: param (optional) - Object with permission type to check
- Returns:
Promise<PermissionStatus> ('PERMISSION_NOT_REQUESTED' | 'PERMISSION_INDETERMINATE' | 'PERMISSION_GRANTED')
-
healthConnectHasPermissions(): Checks if the app has all Health Connect permissions- Platform: Android only
-
healthConnectHasPartialPermissions(): Checks if the app has at least one Health Connect permission- Platform: Android only
-
samsungHealthHasPermissions(): Checks if the app has all Samsung Health permissions- Platform: Android only
-
samsungHealthHasPartialPermissions(): Checks if the app has at least one Samsung Health permission- Platform: Android only
-
androidHasBackgroundPermissions(): Checks if the app has Android background permissions- Platform: Android only
-
shouldRequestAndroidBackgroundPermissions(): Checks if Android background permissions should be requested- Platform: Android only
You may notice that after calling revokeHealthConnectPermissions the permissions are still granted, however they will be revoked the next
time the app is closed (process stops).
Each method will return a promise if the permission window was successfully presented. This value does not indicate whether the user actually granted permission. Please keep in mind that Apple Health does not allow checking the status of permissions for types requested to be read. If the user does not allow data type reading, either by mistake or on purpose, it will simply appear as if there is no data of the requested type in the HealthKit store. Any further changes must be performed by the user through the Apple Health application.
useRookSync
This hook will sync the data according to the options specified
const useRookSync: () => {
sync: (callback: Callback, params?: SyncParams) => void;
syncEvents: (params: SyncEventParams) => Promise<boolean>;
};
sync(callback: Callback, params?: SyncParams): void: Synchronizes health data with or without specific parameters. Uses callbacks to return sync results, including status and errors.- Parameters:
- callback (Callback): Function to execute upon completing the sync operation, receiving SyncResult.
- params (optional): Object containing specific sync parameters, including date, summary, and sources.
- empty: If you only provide a callback, the SDK will sync data from the past 29 days from Health Connect, Apple Health, and Samsung Health.
- options: If you provide a date, summary type, source, and a callback, the SDK will sync data from the specified date, filtered by the selected pillar and source.
- options.date: If you provide only a date, source, and a callback (without summary type), the SDK will sync physical, sleep, and body data from the given date.
- Usage: Allows syncing with defined sources, supporting both Android and iOS platforms.
- Parameters:
syncEvents(params: SyncEventParams): Promise<boolean>: Synchronizes specific health events based on defined parameters. Supports various event types across platforms.- Parameters:
- params: Object containing details for the sync operation, including date, event, and sources.
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>– Resolves to true upon successful completion of the operation. - Usage: Facilitates the synchronization of specific events such as activity, blood_glucose, hydration, etc., and is customizable per platform/OS support.
- Parameters:
Types
export type SyncParams = {
date: string;
summary?: SyncSummaryType;
sources: SDKDataSource[];
};
export type SyncEventParams = {
date: string;
event: SyncEventType;
sources: SDKDataSource[];
};
export type SyncSummaryType = 'sleep' | 'body' | 'physical';
export type SyncResult = {
healthConnect?: SyncSourceResult;
appleHealth?: SyncSourceResult;
samsungHealth?: SyncSourceResult;
};
export type SyncSourceResult = {
status: boolean;
error: Error | { domain: string };
};
export type Callback = (result: SyncResult) => void;
type SyncEventType =
| 'activity'
| 'blood_glucose'
| 'blood_pressure'
| 'body_metrics'
| 'heart_rate'
| 'hydration'
| 'nutrition'
| 'oxygenation'
| 'temperature'
| 'steps'
| 'calories';
export type SyncIOSEventType =
| 'activityEvent'
| 'heartRate'
| 'oxygenation'
| 'temperature'
| 'bloodPressure'
| 'bloodGlucose'
| 'bodyMetrics';
useRookSummaries
This hook is deprecated and will be deleted in upcoming versions, use insted useRookSync.
This hook will help you to extract and send data from apple health to Rook servers.
const useRookSummaries: () => {
ready: boolean;
syncSleepSummary: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncPhysicalSummary: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncBodySummary: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
reSyncFailedSummaries: () => Promise<void>;
};
ready: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.syncSleepSummary: Send the summary to rook servers.syncBodySummary: Send the summary to rook servers.syncPhysicalSummary: Send the summary to rook servers.reSyncFailedSummaries: In case you try to sync a summary and fail, this function help to try to send again.
useRookEvents
This hook is deprecated and will be deleted in upcoming versions, use insted useRookSync.
This hook will help you to extract and send data from apple health to Rook servers.
export type CaloriesResult = {
basal: number;
active: number;
};
const useRookEvents: () => {
ready: boolean;
syncBodyHeartRateEvent: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncPhysicalHeartRateEvent: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncBodyOxygenationEvent: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncPhysicalOxygenationEvent: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncTrainingEvent: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncTemperatureEvent: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncBloodPressureEvent: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncBloodGlucoseEvent: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncBodyMetricsEvent: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncHealthConnectHydrationEvents: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncHealthConnectNutritionEvents: (date: string) => Promise<void>;
syncTodayCaloriesCount: () => Promise<CaloriesResult>;
reSyncFailedEvents: () => Promise<void>;
};
ready: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.syncBodyHeartRateEvents: Send body heart rate events for the specified date.syncPhysicalHeartRateEvents: Send physical heart rate events for the specified date.syncBodyOxygenationEvents: Send body oxygenation events for the specified date.syncPhysicalOxygenationEvents: Send physical oxygenation events for the specified date.syncTrainingEvent: Send training events for the specified date.syncTemperatureEvent: Send temperature events for the specified date.syncBloodPressureEvent: Send pressure events for the specified date.syncBloodGlucoseEvent: Send glucose events for the specified date.syncHealthConnectHydrationEvents: Send hydration events for the specified date.syncHealthConnectNutritionEvents: Send nutrition events for the specified date.syncBodyMetricsEvent: Send body metrics events for the specified date, like change of weight or height.syncTodayCaloriesCount: Send calories events for the current date.reSyncFailedEvents: Sync all the events that couldn't be sync due to an error
useRookVariables
This hook will extract and return the current value of steps and calories from health connect and apple health.
const useRookVariables: () => {
ready: boolean;
getTodaySteps: (source: SDKDataSource) => Promise<string>;
getTodayCalories: (source: SDKDataSource) => Promise<Calories>;
};
Properties
ready: Boolean indicating whether the ROOK SDK is initialized and ready to accept method calls
Functions
-
getTodaySteps(source: SDKDataSource): Promise<string>: Retrieves the number of steps taken today from the specified data source- Parameters:
- source (SDKDataSource): The data source enum to retrieve steps from (HEALTH_CONNECT, SAMSUNG_HEALTH, or APPLE_HEALTH)
- Returns:
Promise<string>- The number of steps taken today as a string - Platform Support: Cross-platform with source-specific implementations
- Parameters:
-
getTodayCalories(source: SDKDataSource): Promise<Calories>: Retrieves the number of calories burned today from the specified data source- Parameters:
- source (SDKDataSource): The data source eum to retrieve calories from (HEALTH_CONNECT, SAMSUNG_HEALTH, or APPLE_HEALTH)
- Returns:
Promise<Calories>- Object containing active and basal calories - Platform Support: Cross-platform with source-specific implementations for Health Connect/Apple Health vs Samsung Health
- Parameters:
useRookDataSources
This hook enables you to access available ROOK data sources by requesting a JSON object with the information or by displaying a basic view with a set of buttons.
For SDK-based data sources (e.g., Apple Health, Health Connect), authorized indicates if the user was created via SDK and linked with ROOK, but it does not confirm permission to access data.
For API-based data sources (e.g., Fitbit, Garmin, Withings), authorized: true confirms that the user has granted ROOK access to retrieve their data through the respective third-party platform.
export interface DataSource {
name: string;
authorizationURL: string;
imageUrl: string;
description: string;
connected: boolean;
}
type options = {
redirectURL?: string;
};
export interface AuthorizedSources {
oura: boolean;
polar: boolean;
whoop: boolean;
fitbit: boolean;
garmin: boolean;
withings: boolean;
google_fit: boolean;
apple_health: boolean;
health_connect: boolean;
android: boolean;
}
export type DataSourceAuthorizer = {
dataSource: DataSourceType;
authorized: boolean;
authorizationUrl?: string;
};
const useRookDataSources: () => {
ready: boolean;
getAvailableDataSources: (options?: { redirectURL?: string }) => Promise<DataSource[]>;
presentDataSourceView: (options?: { redirectURL?: string }) => Promise<boolean>;
revokeDataSource: (type: DataSourceType) => Promise<boolean>;
getAuthorizedDataSources: () => Promise<AuthorizedSources>;
getDataSourceAuthorizer: (props: DataSourceProps) => Promise<DataSourceAuthorizer>;
getAuthorizedDataSourcesV2: () => Promise<AuthorizedSource[]>
};
Properties
ready: Boolean indicating whether the ROOK SDK is initialized and ready to accept method calls
Functions
-
getAvailableDataSources(options?: { redirectURL?: string }): Promise<DataSource[]>: DEPRECATED Retrieves all data sources available in ROOK services- Parameters:
- options (optional): Object containing optional redirectURL for post-authorization redirect
- Returns:
Promise<DataSource[]>: Array of available data sources with their connection status and details - Usage: Used to display available third-party integrations to users
- Note: This function is deprecated and should be avoided in new implementations use insted
getAuthorizedDataSourcesV2
- Parameters:
-
presentDataSourceView(options?: { redirectURL?: string }): Promise<boolean>: DEPRECATED Presents or shows a connections page with available data sources- Parameters:
- options (optional): Object containing optional redirectURL for post-authorization redirect
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Success status of presenting the view - Note: This function is deprecated and should be avoided in new implementations insted create your own screen
- Parameters:
-
revokeDataSource(type: DataSourceType): Promise<boolean>- Description: Revokes user authorization for a specific data source
- Parameters:
- type (DataSourceType): The type of data source to revoke ('Garmin', 'Oura', 'Polar', 'Fitbit', 'Withings', 'Whoop')
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Success status of the revocation
- Usage: Used to disconnect users from specific third-party services
-
getAuthorizedDataSources(): Promise<AuthorizedSources>: Returns authorized data sources after checking ROOK services. For Apple Health, Health Connect, and Android, this determines if the user is connected, not if permissions are granted- Returns:
Promise<AuthorizedSources>- Object containing authorization status for each data source - Usage: Used to check which data sources are currently connected for a user
- Returns:
-
getDataSourceAuthorizer(props: DataSourceProps): Promise<DataSourceAuthorizer>: Retrieves authorization status for a specific data source. If not authorized, provides authorization URL. If already authorized, returns authorized: true without URL- Parameters:
- props (DataSourceProps): Object containing dataSource type and optional redirectURL
- Returns:
Promise<DataSourceAuthorizer>- Authorization status and URL if needed - Usage: Used to check authorization status and obtain authorization URLs for specific data sources
- Parameters:
-
getAuthorizedDataSourcesV2(): Promise<AuthorizedSource[]>: Retrieves all data sources available in ROOK services along with their current authorization status.- Parameters: None.
- Returns:
Promise<AuthorizedSource[]>: An array ofAuthorizedSourceobjects, where each object contains the source'sname,imageUrl, and a booleanauthorizedstatus. - Usage: Used to display a list of all available data sources to the user and show which ones they have already authorized.
useRookAndroidBackgroundSteps
This hook will help you to extract and send data from health connect to Rook servers.
const useRookAndroidBackgroundSteps: () => {
ready: boolean;
isStepsAvailable: () => Promise<boolean>;
enableBackgroundAndroidSteps: () => Promise<boolean>;
disableBackgroundAndroidSteps: () => Promise<boolean>;
isBackgroundAndroidStepsActive: () => Promise<boolean>;
syncTodayAndroidStepsCount: () => Promise<string>;
syncTodayHealthConnectStepsCount: () => Promise<string>;
};
Properties
- ready - Boolean indicating whether the ROOK SDK is initialized and ready to accept method calls
Functions
-
isStepsAvailable(): Promise<boolean>: Checks if steps data is available on the Android device- Platform: Android only
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Whether steps data is available for collection - Usage: Use this to verify if the device supports step counting before enabling background steps
-
enableBackgroundAndroidSteps(): Promise<boolean>: Starts collecting steps data in the background during the day- Platform: Android only
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Success status of enabling background step collection - Usage: Call this to begin automatic step counting in the background
-
disableBackgroundAndroidSteps(): Promise<boolean>: Stops the background collection of steps data during the day- Platform: Android only
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Success status of disabling background step collection - Usage: Call this to stop automatic step counting in the background
-
isBackgroundAndroidStepsActive(): Promise<boolean>: Checks if background step collection is currently active- Platform: Android only
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Whether background step collection is currently running - Usage: Use this to check the current status of background step collection
-
syncTodayAndroidStepsCount(): Promise<string>: Retrieves the number of steps taken today from Android's step counter- Platform: Android only
- Returns:
Promise<string>- Today's step count as a string - Usage: Get step count from the device's native step counter
-
syncTodayHealthConnectStepsCount(): Promise<string>: Retrieves the number of steps taken today from Health Connect- Platform: Android only
- Returns:
Promise<string>- Today's step count from Health Connect as a string - Usage: Get step count specifically from Health Connect data source
useRookData
The useRookData hook provides methods for directly querying aggregated health data (Summaries) and specific events (Events) from the device's native health storage (Apple Health, Samsung Health, or Health Connect).
const useRookData: () => {
ready: boolean;
getSleepSummary: (params: {
date: string;
source: SDKDataSource;
}) => Promise<SleepSummary[]>;
getPhysicalSummary: (params: {
date: string;
source: SDKDataSource;
}) => Promise<PhysicalSummary>;
getBodySummary: (params: {
date: string;
source: SDKDataSource;
}) => Promise<BodySummary>;
getActivityEvents: (params: {
date: string;
source: SDKDataSource;
}) => Promise<ActivityEvent[]>;
};
Please be sure to enable Continuous HR measurement on your Galaxy Watch to improve the accuracy of the readings.
Properties
- ready - Boolean indicating whether the ROOK SDK is initialized and ready to accept method calls
Functions
getSleepSummary(params: { date: string, source: SDKDataSource }): Promise<SleepSummary[]>: Retrieves the sleep summary data for a specific day.- Parameters:
- params: An object containing:
- date (string): The date for which to retrieve data, formatted as 'YYYY-MM-DD'.
- source (SDKDataSource): The specific data source to query (e.g., SDKDataSource.SAMSUNG_HEALTH, SDKDataSource.HEALTH_CONNECT, SDKDataSource.APPLE_HEALTH).
- params: An object containing:
- Returns:
Promise<SleepSummary[]>: A promise that resolves to an array of SleepSummary objects. - Usage: Used to fetch detailed sleep data (e.g., sleep stages, duration) for a given date.
- Note: This function automatically selects the correct native module (Apple Health, Samsung Health, or Health Connect) based on the current platform and the source provided.
- Parameters:
getPhysicalSummary(params: { date: string, source: SDKDataSource }): Promise<PhysicalSummary>: Retrieves the physical activity summary for a specific day.- Parameters:
- params: An object containing:
- date (string): The date for which to retrieve data, formatted as 'YYYY-MM-DD'.
- source (SDKDataSource): The specific data source to query.
- params: An object containing:
- Returns:
Promise<PhysicalSummary>: A promise that resolves to a single PhysicalSummary object containing aggregated data like steps, distance, and calories. - Usage: Used to get a high-level overview of the user's physical activity for a given date.
- Note: This function automatically selects the correct native module based on the current platform and the source provided.
- Parameters:
getBodySummary(params: { date: string, source: SDKDataSource }): Promise<BodySummary>: Retrieves the body summary data for a specific day.- Parameters:
- params: An object containing:
- date (string): The date for which to retrieve data, formatted as 'YYYY-MM-DD'.
- source (SDKDataSource): The specific data source to query.
- params: An object containing:
- Returns:
Promise<BodySummary>: A promise that resolves to a single BodySummary object containing data like weight, body fat, etc. - Usage: Used to fetch the user's body measurements recorded on a given date.
- Note: This function automatically selects the correct native module based on the current platform and the source provided.
- Parameters:
getActivityEvents(params: { date: string, source: SDKDataSource }): Promise<ActivityEvent[]>: Retrieves all individual activity events (like workouts) for a specific day.- Parameters:
- params: An object containing:
- date (string): The date for which to retrieve data, formatted as 'YYYY-MM-DD'.
- source (SDKDataSource): The specific data source to query.
- params: An object containing:
- Returns:
Promise<ActivityEvent[]>: A promise that resolves to an array of ActivityEvent objects, each representing a distinct workout or activity. - Usage: Used to get a list of all workouts (e.g., "Running," "Cycling") the user performed on a given date, including details like duration and energy burned.
- Note: This function automatically selects the correct native module based on the current platform and the source provided.
- Parameters:
Additional notes
In order to include correctly the steps services follow this steps:
- Request Permissions
- Enable background Android steps
- Sync Steps
Customizing the foreground service notification
The steps manager uses a foreground Service which requires a notification to be permanently displayed.
To use your own resources you need to reference them in the AndroidManifest.xml file:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<application>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.STEPS_ICON"
android:resource="@drawable/my_custom_icon"/>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.STEPS_TITLE"
android:resource="@string/my_custom_title"/>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.STEPS_CONTENT"
android:resource="@string/my_custom_content"/>
</application>
</manifest>
Starting on Android 13 (SDK 33) this notification can be dismissed without finishing the service associated with it, then the service will be displayed in the active apps section (This may vary depending on device brand).
Additional information
Auto start
After a call to enableBackgroundAndroidSteps if the device is restarted the Foreground service will start after the
user unlocks their device for the first time (This may vary depending on device brand). This behaviour will be stopped
when calling disableBackgroundAndroidSteps.
Considerations
The steps service is designed to always be active but there are certain scenarios where the service could not behave as intended:
- If the user force closes the application from settings, and then restarts their device the service may not be able to restart.
- The steps are scheduled to be uploaded every hour from the time
enableBackgroundAndroidStepswas called, however it's not possible to guarantee the exact execution time as this depends on how the Android System manages the device resources.
useRookAppleHealthVariables
This hook is deprecated and will be deleted in upcoming versions, use insted useRookVariables.
This hook will help you to extract and send data from apple health to Rook servers.
const useRookAppleHealthVariables: () => {
ready: boolean;
getTodaySteps: () => Promise<void>;
};
ready: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.getTodaySteps: Gets the steps accumulated for the current day.
Additional
Health Connect request quota
To maintain optimal system stability and performance, Health Connect imposes rate limits on client connections to the Health Connect API.
It is important for you to understand that every data type in rook-sdk is constructed of multiple health variables like heart rate, steps count, hydration, etc. So when a Sleep Summary is extracted there are multiple calls made to the Health Connect API, and whereas in the last months our efforts have been focused on optimizing and reducing the number of API call required for each data type it's still possible for that limit to be reached, especially while doing multiple extraction in a short amount of time.
Depending on the sync type you chose you must have the following things in mind:
Request quota when syncing data manually
- Extract summaries once daily: Since summaries collect health data from a previous day, there's no need to extract them more than once per day.
- Use what you already have: If you are extracting Physical Events you don’t need to extract Heart Rate Events ( Physical) or Oxygenation Events (Physical) as these are already included in the PhysicalEvent object.
- Only sync the relevant health data for you use case: If you are not interested on individual events and only want to
sync the summary of a specific date, just use the
syncfunctions inuseRookSyncSummaries. - If you already reached the request quota avoid calling any
syncfunction for the next hours so your quota can be recovered.
Request quota when syncing data automatically
scheduleYesterdaySync already takes care of practically all issues and limitations of Health Connect. When the
quota is reached, all pending syncs are canceled, and a recovery timestamp is created. Pending syncs will not resume
until the user re-opens the app after a few hours.
Frequency of syncing with scheduleYesterdaySync
| Health structure | Frequency | Historical range |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep Summary | Each time scheduleYesterdaySync is called | 29 days in the past until yesterday |
| Body Summary | Each time scheduleYesterdaySync is called | 29 days in the past until yesterday |
| Physical Summary | Each time scheduleYesterdaySync is called | 29 days in the past until yesterday |
| Physical Activity | Each time scheduleYesterdaySync is called | 29 days in the past until today |
| Steps | Each time scheduleYesterdaySync is called | Today |
Continuous Upload for iOS
The hook useRookConfiguration helps you to enable or disable continuous data upload. every time a user opens the app, the sdk will try to upload the data from the previous day of the device's current date.
Note: before enable this feature it is necessary to add a user a request permission from apple health
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
enableAppleHealthSync | This method enables the automatic upload of the summaries from the previous day of the current device's date. Every time the user opens the app it will try to upload the summaries, before use this method is necessary to add a user id and request permissions. |
disableAppleHealthSync | This method disables the automatic upload of the summaries from the previous day of the current device's date. |
Background Upload for iOS
useRookAppleHealth
The hook useRookAppleHealth helps to enable background upload for summaries, this allows to your app to upload health data while your app is in background. it is recommended to combine continuous upload, background upload and manual sync for a better performance.
const useRookAppleHealth = () => {
ready: boolean;
enableBackGroundUpdates: () => Promise<boolean>;
disableBackGroundUpdates: () => Promise<boolean>;
isBackGroundForSummariesEnable: () => Promise<boolean>;
isBackGroundForEventsEnable: () => Promise<void>;
}
Properties
- ready - Boolean indicating whether the ROOK SDK is initialized and ready to accept method calls
Functions
-
enableBackGroundUpdates(): Promise<boolean>- Description: Enables background updates for Apple Health data collection
- Platform: iOS only
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Success status of enabling background updates - Usage: Call this to allow the app to receive health data updates in the background
-
disableBackGroundUpdates(): Promise<boolean>- Description: Disables background updates for Apple Health data collection
- Platform: iOS only
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Success status of disabling background updates - Usage: Call this to stop receiving health data updates in the background
-
isBackGroundForSummariesEnable(): Promise<boolean>- Description: Checks if background updates are enabled for health summaries
- Platform: iOS only
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Whether background summary updates are enabled - Usage: Use this to verify if background summary collection is currently active
-
isBackGroundForEventsEnable(): Promise<void>- Description: Checks if background updates are enabled for health events
- Platform: iOS only
- Returns:
Promise<void>- Completion status of the check - Usage: Use this to verify if background event collection is currently active
For security, iOS devices encrypt the HealthKit storage when users lock their devices. As a result, apps may not be able to read data from Apple Health when it runs in the background. Please refer to the official documentation for more information.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
disableBackGroundUpdates | This method enables the background upload of the summaries. |
disableBackGroundUpdates | This method disables the background upload of the summaries. |
To configure background upload you need to follow the steps bellow:
- Add health kit to your project and enable background delivery.
- Add Background modes and enable Background fetch.
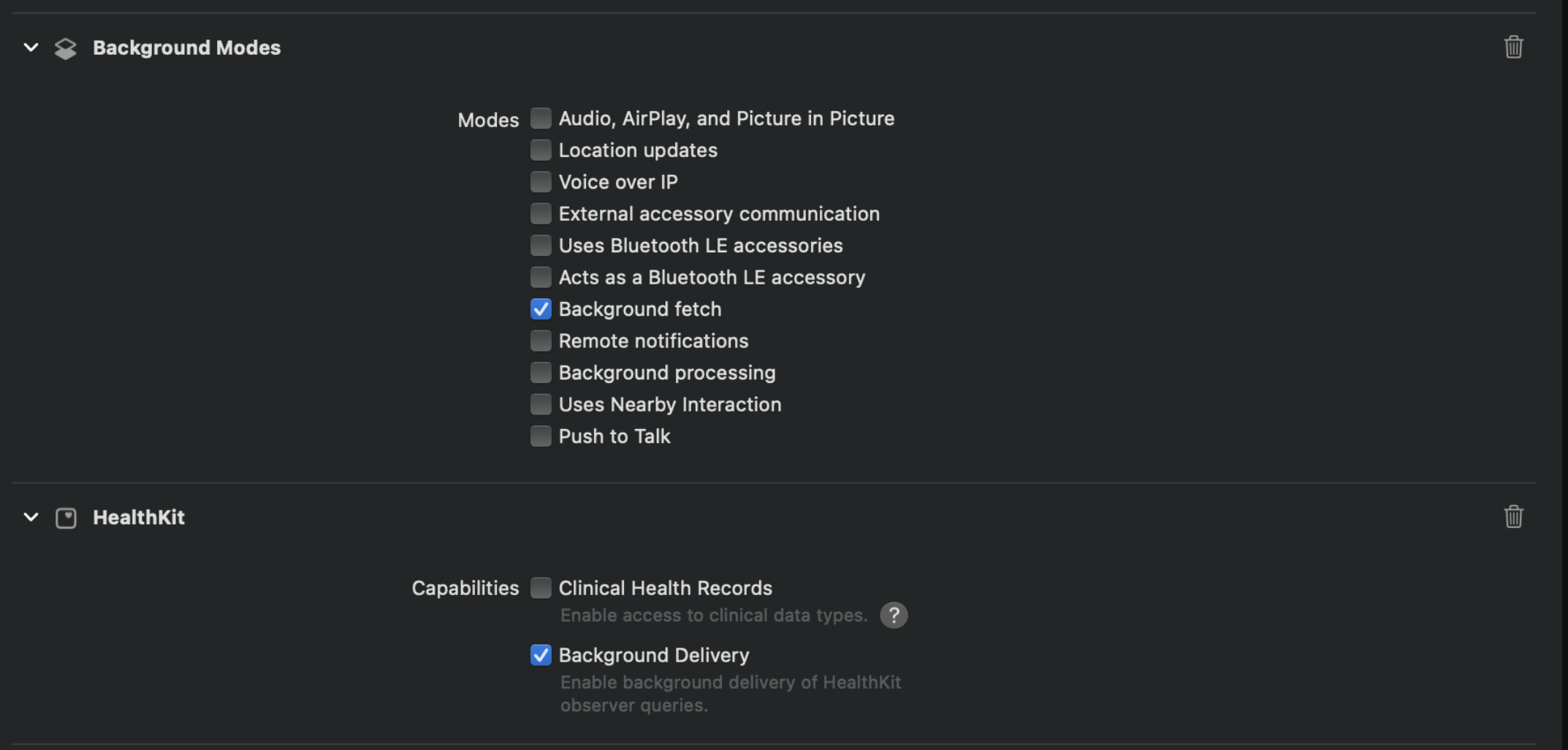
- In the app delegate of your app add the
setBackListenersmethod in didFinishLaunchingWithOptions function.
Example
#import "AppDelegate.h"
#import "RookSDK/RookSDK-Swift.h"
#import <React/RCTBundleURLProvider.h>
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions
{
self.moduleName = @"RookSdkAppleHealthExample";
// You can add your custom initial props in the dictionary below.
// They will be passed down to the ViewController used by React Native.
self.initialProps = @{};
[[RookBackGroundSync shared] setBackListeners];
return [super application:application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:launchOptions];
}
- (NSURL *)sourceURLForBridge:(RCTBridge *)bridge
{
#if DEBUG
return [[RCTBundleURLProvider sharedSettings] jsBundleURLForBundleRoot:@"index"];
#else
return [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"main" withExtension:@"jsbundle"];
#endif
}
@end
Background Upload for Android
If you want to delegate the selection and initiation of the appropriate automatic sync method, please refer to Fundamentals/Configure Background.
Sync health data in background (android 15+)
To sync health data in background, use the scheduleBackgroundSync function during your app's initialization phase.
const useRookHealthConnect: () => {
ready: boolean;
isBackgroundSyncEnabled: () => Promise<boolean>;
scheduleBackgroundSync: () => Promise<boolean>;
cancelBackgroundSync: () => Promise<boolean>;
};
Properties
- ready - Boolean indicating whether the ROOK SDK is initialized and ready to accept method calls
Functions
-
scheduleBackgroundSync(): Promise<boolean>: Schedules the background synchronization of health data using ROOK. Enables automatic background data synchronization with ROOK's API based on defined configuration- Platform: Android only
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Success status of scheduling the background sync - Usage: Call this to enable automatic periodic fetching and sending of health data to ROOK's API in the background
-
cancelBackgroundSync(): Promise<boolean>: Cancels the scheduled background synchronization of health data. Stops the automatic background sync previously scheduled using ROOK- Platform: Android only
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Success status of canceling the background sync - Usage: Call this to stop automatic health data synchronization until scheduled again
isBackgroundSyncEnabled(): Promise<boolean>: Check if the background sync of health connect is active or not.
- Platform: Android Only
- Returns:
Promise<boolean>- Success indicates the background sync is enabled - Usage: Call this to check the status of the background sync
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
import { View } from "react-native";
import { useRookHealthConnect } from "react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect";
function MyComponent() {
const { scheduleBackgroundSync } = useRookHealthConnect();
useEffect(() => {
tryToStartBackgroundSync();
}, []);
const tryToStartBackgroundSync = async () => {
console.log("Attempting to enable background sync...");
try {
await scheduleBackgroundSync();
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
};
return <View>{/* Your UI components here */}</View>;
}
export default MyComponent;
Sync health data automatically (android 14-)
To automatically sync health data, use the scheduleYesterdaySync function during your app's initialization phase.
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
import { View } from "react-native";
import { useRookSyncConfiguration } from "react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect";
function MyComponent() {
const { scheduleYesterdaySync } = useRookSyncConfiguration();
useEffect(() => {
tryToEnableYesterdaySync();
}, []);
const tryToEnableYesterdaySync = async () => {
console.log("Attempting to enable yesterday sync...");
try {
await scheduleYesterdaySync();
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
};
return <View>{/* Your UI components here */}</View>;
}
export default MyComponent;
RookYesterdaySyncPermissions
scheduleYesterdaySync Requires 2 types of permissions
- Android
- POST_NOTIFICATIONS
- FOREGROUND_SERVICE
- FOREGROUND_SERVICE_HEALTH
- ACTIVITY_RECOGNITION
- Health Connect
- SLEEP
- PHYSICAL
- BODY
To request or check both types of permissions, you need to request permissions for Health Connect with useRookSyncPermissions().requestPermissions() to access Health Connect data and useRookSyncPermissions().requestAndroidBackgroundPermissions() to access the background services.
Customizing the foreground service notification
To sync health data automatically, a Foreground Service is used. This service requires a notification to be displayed until the synchronization finishes.
To use your own resources, you need to reference them in the AndroidManifest.xml file:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<application>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.SYNC_ICON"
android:resource="@drawable/my_custom_icon"/>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.SYNC_TITLE"
android:resource="@string/my_custom_title"/>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.SYNC_CONTENT"
android:resource="@string/my_custom_content"/>
</application>
</manifest>
Starting on Android 13 (SDK 33) this notification can be dismissed without finishing the service associated with it, then the service will be displayed in the active apps section (This may vary depending on device brand).
Launch/Stop conditions
scheduleYesterdaySync won't start or will stop if one the following conditions are meet:
- The device battery is low
- The device storage is low
- The device is not connected to the internet
- The user hasn't granted Android Permissions (POST_NOTIFICATIONS, FOREGROUND_SERVICE, FOREGROUND_SERVICE_HEALTH)
- The device has previously exceeded the Health Connect request quota and the recovery timestamp hasn't been meet
- The user hasn't granted Health Connect Permissions (SLEEP, PHYSICAL, BODY)
- The most recent request exceeded the Health Connect request quota
- The userID hasn't been configured
- There is an error initializing the SDK
Background Upload for Samsung
To enable background sync for samsung please refer to useRookConfiguration to enable it with enableSamsungSync
Customizing permissions for Health Connect
If you want to reduce the Health Connect permissions used by this SDK you can do it following the manifest merge documentation and the SDK will change the behavior of request/check permissions functions based on the declared permissions:
For example if you remove the READ_MENSTRUATION permission...
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<uses-permission
android:name="android.permission.health.READ_MENSTRUATION"
tools:node="remove"/>
</manifest>
the functions checkHealthConnectPermissions and requestHealthConnectPermissions will check/request all permissions
excluding READ_MENSTRUATION
Note that this process only works for removing Health Connect permissions, adding a permission that is not included in the default list will do nothing.
Health Connect permissions are declared with the syntax: android.permission.health.READ.., to see the current Health Connect permissions go to you AndroidManifest and select the merged manifest tab.