RookSDK
If you’re building a health or fitness application of any kind, you likely understand the power of health user data. Integrating it with your application will benefit you regardless of your use case, whether it’s mindfulness and wellness, digital health, or remote care.
Apple Health does not have an API, and since no data is stored in the cloud, you need to retrieve it locally from your users' devices. This can be done by implementing Apple HealthKit and its data retrieval methods into your iOS app.
ROOK SDK allows developers to ask their users to access and share their health data through Apple HealthKit.
ROOK SDK for iOS enables fetching health data from Apple Health and synchronizing it with the ROOK server. It also allows registering a new user and storing this information locally.
The SDK provides access to Apple Health data, but only after the user's explicit consent. Users can select detailed data sharing settings, including which data types will be read.
Demo app
To help your implementation here is a demo app that shows you how to configure and use the sdk: https://github.com/RookeriesDevelopment/rook_demo_app_ios_rook_sdk
Features
The features listed bellow are available to fetch and synchronize:
- Sleep summaries
- Physical summaries
- Body summaries
- Heart rate events
- Oxygenation events
- Activity events
- Temperature Events
- Blood Glucose Events
- Blood Pressure Events
- Time zone of the device
- Variable extraction
- Background active extraction
Integrating the iOS framework
Installation
The SDK requires Xcode 16.0.0 or higher. To run your app using the Rook SDK on a connected device with iOS 13.0 or later you need Xcode 16.0 or higher.
To add a package dependency to your Xcode project, select File > Swift Packages > Add Package Dependency and enter the repository URL rook SDK
Rook SDK supports installation with CocoaPods
Here's how to install Rook using CocoaPods:
- Create a Podfile if you don't already have one. From the root of your project directory, run the following command:
pod init
- To your Podfile, add the Rook pod
pod "RookSDK"
- Install the pods, then open your .xcworkspace file to see the project in Xcode:
pod install
Configuration
To configure Rook SDK, you need to follow this steps:
- Import the apple health sdk
import RookSDK
- Add your credentials.
- This method should be called at the beginning of your app's launch process.
func application(_ application: UIApplication
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey : Any]? = nil) -> Bool {
RookConnectConfigurationManager.shared.setConfiguration(
clientUUID: "YOUR-CLIENT-UUID",
secretKey: "YOUR-SECRET-KEY",
enableBackgroundSync: true,
enableEventsBackgroundSync: true)
RookConnectConfigurationManager.shared.setEnvironment(.sandbox)
RookConnectConfigurationManager.shared.initRook()
return true
}
- Add the HealthKit framework to your Xcode project:
- Open your project in Xcode.
- Click on your project file in the Project Navigator.
- Select your target and then click on the "Build Phases" tab.
- Click on the "+" button under the "Link Binary With Libraries" section and select "HealthKit.framework" from the list.
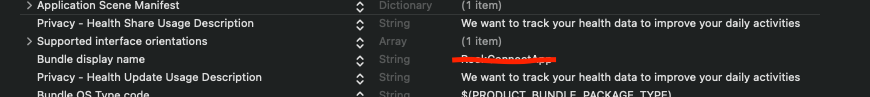
- Then declare the privacy permissions used by this SDK. You will need to include the NSHealthShareUsageDescription and NSHealthUpdateUsageDescription keys in your app's Info.plist file. These keys provide a description of why your app needs to access HealthKit data and will be displayed to the user in the permission request dialog.
<key>NSHealthShareUsageDescription</key>
<string>This app requires access to your health and fitness data in order to track your workouts and activity levels.</string>
<key>NSHealthUpdateUsageDescription</key>
<string>This app requires permission to write health data to HealthKit.</string>
RookConnectConfigurationManager Use this class to configure and init the sdk. This class conforms the singleton pattern, to access this class use the shared property.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
func setConfiguration(clientUUID: String, secretKey: String, enableBackgroundSync: Bool, enableEventsBackgroundSync: Bool) | Sets the configuration of the sdk. |
func setEnvironment(_ environment: RookEnvironment) | Configures the rook sdk environment. |
func initRook() | Initializes the rook sdk |
func updateUserId(_ id: String, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | It will try to register the user in the rook server and it will be stored, if the registration was successful, after that the sdk upload the current time zone of the device. |
func getUserId(completion: @escaping (Result<String, Error>) -> Void) | Returns the user id stored locally. |
func clearUser(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Deletes the user stored locally. |
func removeUserFromRook(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Removes the authorization od the user to upload data from apple health and deletes the user id stored locally. |
func syncUserTimeZone(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Uploads the current time zone of the device a user has to added before use this method. |
func enableSync() | This method enables the automatic upload of the missing summaries from previous days. Every time the user opens the app it will try to upload the summaries, before use this method is necessary to add a user id and request all permissions. |
func disableSync() | This method disables the automatic upload of the summaries from the previous days. |
func isSyncEnable() -> Bool | Returns a boolean indicating if the automatic upload is enable. |
func setConsoleLogAvailable(_ value: Bool) | Enables or disables console logs for transmission responses when uploading events or summaries. |
The parameters enableBackgroundSync and enableEventsBackgroundSync enable background synchronization for summaries and events, respectively. To disable synchronization for either, set the corresponding parameter to false.
Get user authorization
Before you can retrieve any data, your app needs to be authorized to access Apple Health data by your users. To get authorization, use the authorize method, and the corresponding dialog will be shown on top of your app.
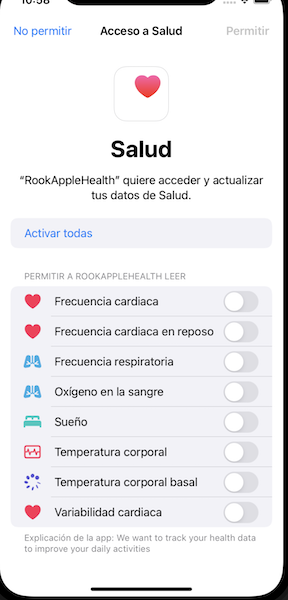
The SDK provides the RookConnectPermissionsManager class to request user permission. It contains the following methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
+ requestAllPermissions(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Sends a request for all the health permissions and displays a view to grand access |
+ requestSleepPermissions(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Sends a request for the sleep data types permissions and displays a view to grand access. |
+ requestUserInfoPermissions(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Sends a request for the user information permissions. |
+ requestPhysicalPermissions(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Sends a request for the physical data types permissions and displays a view to grand access |
+ requestBodyPermissions(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Sends a request for the body data type permissions and displays a view to grand access. |
+ requestPermissions(_ permissions: [HealthDataType]?, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Sends a request for the permissions given and displays a view to grand access. |
The callback of each method returns a boolean: true if the permission window was successfully presented, or false with an optional error if the window was not presented properly. This value does not indicate whether the user actually granted permission. Please keep in mind that Apple Health does not allow checking the status of permissions for types requested to be read. If the user does not allow data type reading, either by mistake or on purpose, it will simply appear as if there is no data of the requested type in the HealthKit store. Any further changes must be performed by the user through the Apple Health application.
If you use requestPermissions(_ permissions: [HealthDataType]?, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) to request for permissions, it is recommended to add the following data types, this will allow RookSDK to work propertly: stepCount, height, bodyMass, heartRate, heartRateVariabilitySDNN, workout, sleepAnalysis, oxygenSaturation.
The list of the variable type available to request permission and check status
| Name |
|---|
appleExerciseTime |
appleMoveTime |
appleStandTime |
basalEnergyBurned |
activeEnergyBurned |
stepCount |
distanceCycling |
distanceWalkingRunning |
distanceSwimming |
swimmingStrokeCount |
flightsClimbed |
walkingSpeed |
walkingStepLength |
runningPower |
runningSpeed |
height |
bodyMass |
bodyMassIndex |
waistCircumference |
bodyFatPercentage |
bodyTemperature |
basalBodyTemperature |
appleSleepingWristTemperature |
heartRate |
restingHeartRate |
walkingHeartRateAverage |
heartRateVariabilitySDNN |
electrocardiogram |
workout |
sleepAnalysis |
sleepApneaEvent |
vo2Max |
oxygenSaturation |
respiratoryRate |
uvExposure |
biologicalSex |
dateOfBirth |
bloodPressureSystolic |
bloodPressureDiastolic |
bloodGlucose |
dietaryEnergyConsumed |
dietaryProtein |
dietarySugar |
dietaryFatTotal |
dietaryCarbohydrates |
dietaryFiber |
dietarySodium |
dietaryCholesterol |
User
Before synchronize summaries or events a user have to be added, otherwise the sdk will return an error.
The class UserManager contains the below methods related to the user access.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
func updateUserId(_ id: String, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | It will try to register the user in the rook server and it will be stored, if the registration was successful, after that the sdk upload the current time zone of the device. |
func getUserId(completion: @escaping (Result<String, Error>) -> Void) | Return the user id stored locally. |
func clearUser(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Deletes the user stored locally. |
func removeUserFromRook(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Removes the authorization od the user to upload data from apple health and deletes the user id stored locally. |
public func syncUserTimeZone(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Uploads the current time zone of the device a user has to added before use this method. |
func revokeDataSource(dataSource: DataSourceRevoke, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Revoke the authorization of the data source given. |
Async await is supported.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
public func updateUserId(_ id: String) async throws -> Bool | It will try to register the user in the rook server and it will be stored, if the registration was successful, after that the sdk upload the current time zone of the device. |
public func getUserId() async throws -> String | Return the user id stored locally. |
public func clearUser() async throws -> Bool | Deletes the user stored locally. |
public func removeUserFromRook() async throws -> Bool | Removes the authorization od the user to upload data from apple health and deletes the user id stored locally. |
public func syncUserTimeZone() async throws -> Bool | Uploads the current time zone of the device a user has to added before use this method. |
func revokeDataSource(dataSource: DataSourceRevoke) async throws -> Bool | Revoke the authorization of the data source given. |
Any call to updateUserId with a different userId will override the previous userID and reset the sync status, if
you are using BackgroundSync all health data will synchronize
again the next time the app is launched.
Continuous Upload
The class RookConnectConfigurationManager contains two methods to enable or disable continuous data upload. every time a user opens the app, the sdk will try to upload the data from the previous day of the device's current date.
Note: before enable this feature it is necessary to add a user a request permission from apple health
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
func enableSync() | This method enables the automatic upload, it will check the last time data was synced. If there is new data to update or pending data from previous days, it will upload this information., before use this method is necessary to add a user id and request permissions. |
func disableSync() | This method disables the automatic upload of the summaries. |
Background Upload
RookBackGroundSync
The class RookBackGroundSync contains methods to enable background uploads for summaries, allowing your app to upload health data while it is in the background. It is recommended to combine continuous upload, background upload, and manual sync for better performance.
For security, iOS devices encrypt the HealthKit storage when users lock their devices. As a result, apps may not be able to read data from Apple Health when running in the background. Please refer to the official documentation for more information.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
func setBackListeners() | This method has to be added in app delegate to enable back ground upload. |
func enableBackGroundForSummaries() | This method enables the background upload of the summaries. |
func disableBackGroundForSummaries() | This method disables the background upload of the summaries. |
func isBackGroundForEventsEnable() -> Bool | This method returns the status of background upload for summaries. |
func enableBackGroundForEvents() | This method enables the background upload of the events. |
func disableBackGroundForEvents() | This method disables the background upload of the events. |
func isBackGroundForEventsEnable() -> Bool | This method returns the status of background upload for events. |
To configure background upload you need to follow the steps bellow:
- Add health kit to your project and enable background delivery.
- Add Background modes and enable Background fetch.
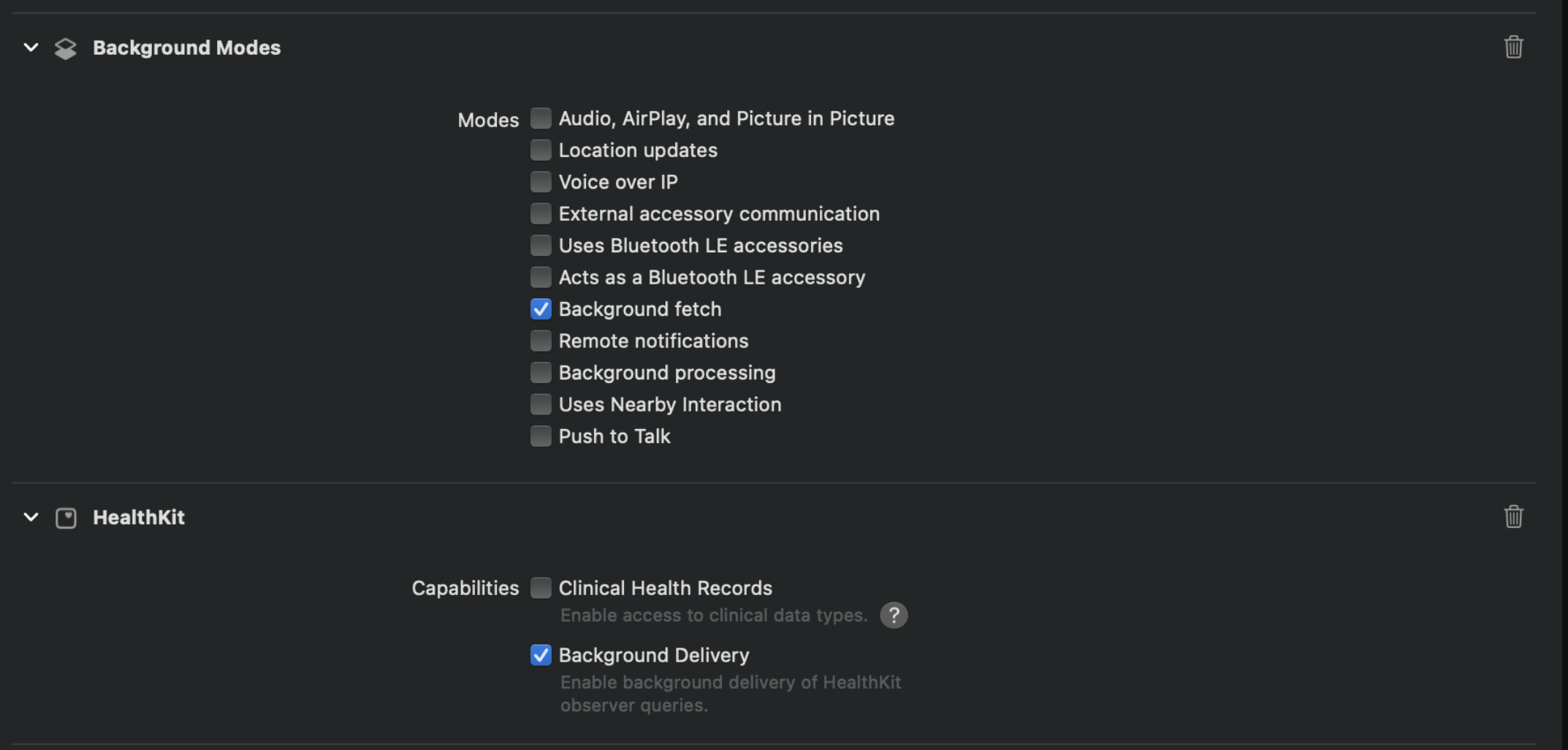
- In the app delegate of your app add the
setBackListeners()method in didFinishLaunchingWithOptions function.
Example
import RookSDK
class AppDelegate: NSObject, UIApplicationDelegate {
func application(_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey : Any]? = nil) -> Bool {
RookBackGroundSync.shared.setBackListeners()
}
Background notifications error
When an error occurs in a back ground proccess, it can be listen by adding an observer, as shown in the example below:
import RookSDK
func onAppear() {
NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(
self,
selector: #selector(handleErrorBackground),
name: NSNotification.Name.init(EventNames.errorBackGround),
object: nil)
}
@objc private func handleErrorBackground(_ notification: Notification) {
if let data: [AnyHashable : Any] = notification.userInfo {
debugPrint(data)
}
}
Manual Sync Data
RookSummaryManager
This class contains the methods to synchronize summaries of the user
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
func sync(completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Uploads the sleep, physical and body summaries of previous days that has no been uploaded. |
func sync(_ date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Fetches and uploads sleep, physical, and body summary data for the specified date. |
func sync(_ date: Date, summaryType: [SummaryTypeToUpload], completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Fetches and uploads the summary or summaries given for the specified date. |
func getSleepSummary(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<[RookSleepSummary], Error>) -> Void) | Returns an array of the sleep summaries after upload the summary or summaries for the specified date. |
func getPhysicalSummary(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<RookPhysicalSummary, Error>) -> Void) | Returns the physical summary after upload the summary for the specified date. |
func getBodySummary(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<RookBodySummary, Error>) -> Void) | Returns the physical body after upload the summary for the specified date. |
Async await implementation is also supported
The bellow object represents the sleep summary returned by getSleepSummary:
public struct RookSleepSummary: Encodable {
public let datetime: Date
public let sourceOfData: String
public let sleepHealthScore: Int?
public let sleepStartDatetime, sleepEndDatetime, sleepDate: Date
public let sleepDurationSeconds, timeInBedSeconds, lightSleepDurationSeconds, remSleepDurationSeconds: Int?
public let deepSleepDurationSeconds, timeToFallAsleepSeconds, timeAwakeDuringSleepSeconds, sleepQualityRating1_5_Score: Int?
public let sleepEfficiency1_100_Score, sleepGoalSeconds, sleepContinuity1_5_Score, sleepContinuity1_5_Rating: Int?
public let hrMaxBPM, hrMinimumBPM, hrAvgBPM, hrRestingBPM: Int?
public let hrBasalBPM: Int?
public let hrGranularDataBPM: [RookHearRateGranular]?
public let hrvAvgRmssdNumber, hrvAvgSdnnNumber: Int?
public let hrvSdnnGranularData: [RookHRVSDNNGranular]?
public let hrvRmssdGranularData: [RookHRVRmssdGranular]?
public let temperatureMinimumCelsius, temperatureAvgCelsius, temperatureMaxCelsius: [RookTemperature]?
public let temperatureGranularDataCelsius: [RookTemperatureGranular]?
public let temperatureDeltaCelsius: [RookTemperature]?
public let breathsMinimumPerMin, breathsAvgPerMin, breathsMaxPerMin: Int?
public let breathingGranularDataBreathsPerMin: [RookBreatingGranular]?
public let snoringEventsCountNumber, snoringDurationTotalSeconds: Int?
public let snoringGranularDataSnores: [RookSnoringGranular]?
public let saturationAvgPercentage: Int?
public let saturationGranularDataPercentage: [RookSaturationGranular]?
public let saturationMinPercentage, saturationMaxPercentage: Int?
public let apneaEvents: [RookApneaEvent]?
public let sleepSamples: [RookSleepZoneSample]?
public let maxWristTemperature: Double?
public let minWristTemperature: Double?
public let averageWristTemperature: Double?
public let granularWristTemperatureData: [AppleWristTemperatureSample]?
}
public struct RookHearRateGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let hrBPM: Int
}
public struct RookHRVSDNNGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let hrvSDNN: Double
}
public struct RookHRVRmssdGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let hrvRmssd: Int
}
public struct RookTemperature: Encodable {
let temperatureCelsius: Int
let measurementType: String
}
public struct RookTemperatureGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let temperatureCelsius: Int
public let measurementType: String
}
public struct RookBreatingGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let breathsPerMin: Int
}
public struct RookSnoringGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds: Int
public let snoringEventsCountNumber: Int
}
public struct RookSaturationGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let saturationPercentage: Int
}
public struct RookApneaEvent: Encodable {
public let startDate: Date
public let endDate: Date
public let duration: Double
public let appleValue: Int
}
public struct RookSleepZoneSample: Encodable {
public let startDate: Date
public let endDate: Date
public let duration: Double
public let zone: String
}
public struct AppleWristTemperatureSample: Encodable {
public let startDate: Date
public let endDate: Date
public let value: Double
}
The following variables are injected by an apple watch when a sleep schedule has been added: is the watch is been used while sleeping.
- sourceOfData
- sleepStartDatetime
- sleepEndDatetime
- sleepDate
- sleepDurationSeconds
- timeInBedSeconds
- lightSleepDurationSeconds
- remSleepDurationSeconds
- deepSleepDurationSeconds
- hrMaxBPM
- hrMinimumBPM
- hrAvgBPM
- hrBasalBPM
- hrGranularDataBPM
- hrvAvgSdnnNumber
- hrvSdnnGranularData
- breathsMinimumPerMin
- breathsAvgPerMin
- breathsMaxPerMin
- breathingGranularDataBreathsPerMin
- saturationAvgPercentage
- saturationGranularDataPercentage
- saturationMinPercentage
- saturationMaxPercentage
- apneaEvents
- sleepSamples
- maxWristTemperature
- minWristTemperature
- averageWristTemperature
- granularWristTemperatureData
The bellow object represents the physical summary returned by getPhysicalSummary:
public struct RookPhysicalSummary: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let physicalHealthScore: Int?
public let stepsPerDayNumber: Int?
public let stepsGranularDataStepsPerHr: [RookStepsGranular]?
public let activeStepsPerDayNumber: Int?
public let activeStepsGranularDataStepsPerHr: [RookStepsGranular]?
public let walkedDistanceMeters: Int?
public let traveledDistanceMeters: Int?
public let cyclingDistanceMeters: Int?
public let traveledDistanceGranularDataMeters: [RookTraveledDistanceGranular]?
public let floorsClimbedNumber: Int?
public let floorsClimbedGranularDataFloors: [RookFloorsClimbedGranular]?
public let elevationAvgAltitudeMeters: Int?
public let elevationMinimumAltitudeMeters: Int?
public let elevationMaxAltitudeMeters: Int?
public let elevationLossActualAltitudeMeters: Int?
public let elevationGainActualAltitudeMeters: Int?
public let elevationPlannedGainMeters: Int?
public let elevationGranularDataMeters: [RookElevationGranular]?
public let swimmingStrokesNumber: Int?
public let swimmingNumLapsNumber: Int?
public let swimmingPoolLengthMeters: Int?
public let swimmingTotalDistanceMeters: Int?
public let swimmingDistanceGranularDataMeters: [RookSwimmingDistanceGranular]?
public let saturationAvgPercentage: Int?
public let saturationGranularDataPercentage: [RookSaturationGranular]?
public let vo2MaxMlPerMinPerKg: Double?
public let vo2GranularDataLiterPerMin: [RookVo2Granular]?
public let activeSeconds: Int?
public let restSeconds: Int?
public let lowIntensitySeconds: Int?
public let moderateIntensitySeconds: Int?
public let vigorousIntensitySeconds: Int?
public let inactivitySeconds: Int?
public let continuousInactivePeriodsNumber: Int?
public let activityLevelGranularDataNumber: [RookActivityLevelGranularData]?
public let caloriesNetIntakeKilocalories: Int?
public let caloriesExpenditureKilocalories: Int?
public let caloriesNetActiveKilocalories: Int?
public let caloriesBasalMetabolicRateKilocalories: Int?
public let hrMaxBPM: Int?
public let hrMinimumBPM: Int?
public let hrAvgBPM: Int?
public let hrRestingBPM: Int?
public let hrGranularDataBPM: [RookHearRateGranular]?
public let hrvAvgRmssdNumber: Double?
public let hrvAvgSdnnNumber: Double?
public let hrvSdnnGranularDataNumber: [RookHRVSDNNGranular]?
public let hrvRmssdGranularDataNumber: [RookHRVRmssdGranular]?
public let stressAtRESTDurationSeconds: Int?
public let stressDurationSeconds: Int?
public let lowStressDurationSeconds: Int?
public let mediumStressDurationSeconds: Int?
public let highStressDurationSeconds: Int?
public let stressGranularDataScoreNumber: [RookStressGranular]?
public let stressAvgLevelNumber: Int?
public let stressMaxLevelNumber: Int?
public let walkingSpeed: Int?
public let walkingStepLength: Int?
public let runningPower: Int?
public let runningSpeed: Int?
}
public struct RookStepsGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds: Int
public let steps: Int
}
public struct RookTraveledDistanceGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds: Int
public let traveledDistanceMeters: Int
}
public struct RookFloorsClimbedGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds: Int
public let floorsClimbed: Int
}
public struct RookElevationGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds: Int
public let elevationChange: Int
}
public struct RookSwimmingDistanceGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds: Int
public let swimmingDistanceMeters: Int
}
public struct RookVo2Granular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let vo2MlPerMinPerKg: Double
}
public struct RookActivityLevelGranularData: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let activityLevel: Int
}
public struct RookStressGranular: Encodable {
let dateTime: Date
let stressScore: Int
}
The following variables are injected in a physical summary by an apple watch:
- stepsPerDayNumber
- stepsGranularDataStepsPerHr
- activeStepsPerDayNumber
- activeStepsGranularDataStepsPerHr
- walkedDistanceMeters
- traveledDistanceMeters
- cyclingDistanceMeters
- traveledDistanceGranularDataMeters
- floorsClimbedNumber
- floorsClimbedGranularDataFloors
- swimmingStrokesNumber
- swimmingNumLapsNumber
- swimmingPoolLengthMeters
- swimmingTotalDistanceMeters
- swimmingDistanceGranularDataMeters
- saturationAvgPercentage
- saturationGranularDataPercentage
- vo2MaxMlPerMinPerKg
- vo2GranularDataLiterPerMin
- activeSeconds
- caloriesNetIntakeKilocalories
- caloriesExpenditureKilocalories
- caloriesNetActiveKilocalories
- hrMaxBPM
- hrMinimumBPM
- hrAvgBPM
- hrRestingBPM
- hrGranularDataBPM
- hrvAvgSdnnNumber
- hrvSdnnGranularDataNumber
- walkingSpeed
- walkingStepLength
- runningPower
- runningSpeed
The bellow object represents the body summary returned by getBodySummary:
public struct RookBodySummary: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let bodyHealthScore: Int?
public let waistCircumferenceCMNumber: Int?
public let hipCircumferenceCMNumber: Int?
public let chestCircumferenceCMNumber: Int?
public let boneCompositionPercentageNumber: Int?
public let muscleCompositionPercentageNumber: Int?
public let waterCompositionPercentageNumber: Int?
public let weightKgNumber: Float?
public let heightCMNumber: Float?
public let bmiNumber: Float?
public let bloodGlucoseDayAvgMgPerDLNumber: Double?
public let bloodGlucoseGranularDataMgPerDL: [RookBloodGlucoseGranular]?
public let bloodPressureDayAvgSystolicDiastolicBpNumber: [RookBloodPressureSystolicDiastolic]?
public let bloodPressureGranularDataSystolicDiastolicBpNumber: [RookBloodPressureGranularSystolicDiastolicBp]?
public let waterTotalConsumptionMlNumber: Int?
public let hydrationAmountGranularDataMlNumber: [RookHydrationAmountGranular]?
public let hydrationLevelGranularDataPercentageNumber: [RookHydrationLevelGranular]?
public let hrMaxBPM: Int?
public let hrMinimumBPM: Int?
public let hrAvgBPM: Int?
public let hrRestingBPM: Int?
public let hrGranularDataBPM: [RookHearRateGranular]?
public let hrvAvgRmssdNumber: Double?
public let hrvAvgSdnnNumber: Double?
public let hrvSdnnGranularDataNumber: [RookHRVSDNNGranular]?
public let hrvRmssdGranularDataNumber: [RookHRVRmssdGranular]?
public let moodMinimumScale: Int?
public let moodAvgScale: Int?
public let moodGranularDataScale: [RookMoodGranular]?
public let moodMaxScale: Int?
public let moodDeltaScale: Int?
public let foodIntakeNumber: Int?
public let caloriesIntakeNumber: Int?
public let proteinIntakeGNumber: Int?
public let sugarIntakeGNumber: Int?
public let fatIntakeGNumber: Int?
public let transFatIntakeGNumber: Int?
public let carbohydratesIntakeGNumber: Int?
public let fiberIntakeGNumber: Int?
public let alcoholIntakeGNumber: Int?
public let sodiumIntakeMgNumber: Int?
public let cholesterolIntakeMgNumber: Int?
public let saturationAvgPercentage: Int?
public let saturationGranularDataPercentage: [RookSaturationGranular]?
public let vo2MaxMlPerMinPerKg: Double?
public let vo2GranularDataLiterPerMin: [RookVo2Granular]?
public let temperatureMinimumCelsius: [RookTemperature]?
public let temperatureAvgCelsius: [RookTemperature]?
public let temperatureMaxCelsius: [RookTemperature]?
public let temperatureDeltaCelsius: [RookTemperature]?
public let temperatureGranularDataCelsius: [RookTemperatureGranular]?
public let uvExposureMax: Int?
public let uvExposureAvg: Int?
public let uvExposureMin: Int?
public let uvExposureSeconds: Int?
}
public struct RookBloodGlucoseGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let bloodGlucoseMgPerDL: Double
}
public struct RookBloodPressureSystolicDiastolic: Encodable {
public let systolicBp, diastolicBp: Int
}
public struct RookBloodPressureGranularSystolicDiastolicBp: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let systolicBp, diastolicBp: Int
}
public struct RookHydrationAmountGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds, hydrationAmountMl: Int
}
public struct RookHydrationLevelGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds, hydrationLevelPercentage: Int
}
public struct RookMoodGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds: Int
public let moodScale: Int
}
The following variables are injected by an apple watch:
- hrMaxBPM
- hrMinimumBPM
- hrAvgBPM
- hrRestingBPM
- hrGranularDataBPM
- hrvAvgSdnnNumber
- hrvSdnnGranularDataNumber
- saturationAvgPercentage
- saturationGranularDataPercentage
- vo2MaxMlPerMinPerKg
- vo2GranularDataLiterPerMin
The following variables are injected manually in iOS Health app:
- waistCircumferenceCMNumber
- waterCompositionPercentageNumber
- weightKgNumber
- heightCMNumber
- bmiNumber
- bloodGlucoseDayAvgMgPerDLNumber
- bloodGlucoseGranularDataMgPerDL
- bloodPressureDayAvgSystolicDiastolicBpNumber
- bloodPressureGranularDataSystolicDiastolicBpNumber
- waterTotalConsumptionMlNumber
- hydrationAmountGranularDataMlNumber
- foodIntakeNumber
- caloriesIntakeNumber
- proteinIntakeGNumber
- sugarIntakeGNumber
- fatIntakeGNumber
- carbohydratesIntakeGNumber
- fiberIntakeGNumber
- sodiumIntakeMgNumber
- temperatureMinimumCelsius
- temperatureAvgCelsius
- temperatureMaxCelsius
- temperatureGranularDataCelsius
- uvExposureMax
- uvExposureAvg
- uvExposureMin
- uvExposureSeconds
enum SummaryTypeToUpload {
case sleep
case physical
case body
}
⚠️ Deprecated: The below functions are deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use the functions above instead.
| Method | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
func syncSummaries(completion: @escaping () -> Void) | Uploads the sleep, physical and body summaries of previous days that has no been uploaded. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func syncSleepSummary(form date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronizes the sleep summary from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func syncPhysicalSummary(form date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronizes the physical summary from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func syncBodySummary(from date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronizes the body summary from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
| Method | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
public func syncSummaries() async | Uploads the sleep, physical and body summaries of previous days that has no been uploaded. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
public func syncSleepSummary(from date: Date) async throws -> Bool | Synchronizes the sleep summary from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
public func syncPhysicalSummary(from date: Date) async throws -> Bool | Synchronizes the physical summary from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
public func syncBodySummary(from date: Date) async throws -> Bool | Synchronizes the body summary from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
RookEventsManager
| Method | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
func syncEvents(date: Date, eventType: EventTypeToUpload, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronizes health-related events of a specified type for a given date. This function uploads the selected event data and returns a success or failure result through a completion handler. | Available |
getTodayStepCount(completion: @escaping (Result<Int, Error>) -> Void) | "Upload the current step count retrieved from Apple Health as a steps event, and return the current count or an error in the completion response. | Available |
getTodayCalories(completion: @escaping (Result<RookCalories, Error>) -> Void) | "Upload the current calories burned count retrieved from Apple Health as a calories event, and return the current count in RookCalories object or an error in the completion response. | Available |
func getActivityEvents(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<[RookActivityEvent], Error>) -> Void) | Returns an array of the workout activities after upload them for the specified date. |
Async await implementation is also supported
The bellow object represents the activity event returned by getActivityEvents:
public struct RookActivityEvent: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let sourcesOfData: String?
public let activityStartTimeDateTime: Date
public let activityEndTimeDateTime: Date
public let activityDurationSeconds: Int?
public let activityTypeName: String?
public let activeSeconds: Int?
public let restSeconds: Int?
public let lowIntensitySeconds: Int?
public let moderateIntensitySeconds: Int?
public let vigorousIntensitySeconds: Int?
public let inactivitySeconds: Int?
public let activityLevelGranularDataNumber: [RookActivityLevelGranularData]?
public let continuousInactivePeriodsNumber: Int?
public let activityStrainLevelNumber: Int?
public let activityWorkKilojoules: Int?
public let activityEnergyKilojoules: Int?
public let activityEnergyPlannedKilojoules: Int?
public let caloriesNetIntakeKilocalories: Int?
public let caloriesExpenditureKilocalories: Float?
public let caloriesNetActiveKilocalories: Float?
public let caloriesBasalMetabolicRateKilocalories: Float?
public let fatPercentageOfCaloriesPercentage: Int?
public let carbohydratePercentageOfCaloriesPercentage: Int?
public let proteinPercentageOfCaloriesPercentage: Int?
public let stepsNumber: Int?
public let stepsGranularDataStepsPerMin: [RookStepsGranular]?
public let walkedDistanceMeters, traveledDistanceMeters: Int?
public let traveledDistanceGranularDataMeters: [RookTraveledDistanceGranular]?
public let floorsClimbedNumber: Int?
public let floorsClimbedGranularDataFloorsNumber: [RookFloorsClimbedGranular]?
public let elevationAvgAltitudeMeters, elevationMinimumAltitudeMeters, elevationMaxAltitudeMeters, elevationLossActualAltitudeMeters: Int?
public let elevationGainActualAltitudeMeters, elevationPlannedGainMeters: Int?
public let elevationGranularDataMeters: [RookElevationGranular]?
public let swimmingNumStrokesNumber, swimmingNumLapsNumber, swimmingPoolLengthMeters, swimmingTotalDistanceMeters: Int?
public let swimmingDistanceGranularDataMeters: [RookSwimmingDistanceGranular]?
public let hrMaxBPM, hrMinimumBPM, hrAvgBPM, hrRestingBPM: Int?
public let hrGranularDataBPM: [RookHearRateGranular]?
public let hrvAvgRmssdNumber, hrvAvgSdnnNumber: Double?
public let hrvSdnnGranularDataNumber: [RookHRVSDNNGranular]?
public let hrvRmssdGranularDataNumber: [RookHRVRmssdGranular]?
public let speedNormalizedMetersPerSecond, speedAvgMetersPerSecond, speedMaxMetersPerSecond: Int?
public let speedGranularDataMetersPerSecond: [RookSpeedGranular]?
public let velocityVectorAvgSpeedAndDirection, velocityVectorMaxSpeedAndDirection: [RookVelocityVectorSpeed]?
public let paceAvgMinutesPerKilometer, paceMaxMinutesPerKilometer, cadenceAvgRPM, cadenceMaxRPM: Int?
public let cadenceGranularDataRPM: [RookCadenceGranular]?
public let torqueAvgNewtonMeters, torqueMaxNewtonMeters: Int?
public let torqueGranularDataNewtonMeters: [RookTorqueGranular]?
public let lapGranularDataLapsNumber: [RookLapGranular]?
public let powerAvgWattsNumber, powerMaxWattsNumber: Int?
public let powerGranularDataWattsNumber: [RookPowerGranular]?
public let positionStartLatLngDeg, positionCentroidLatLngDeg, positionEndLatLngDeg: [RookPositionLatLng]?
public let positionGranularDataLatLngDeg: [RookPositionGranular]?
public let positionPolylineMapDataSummaryString: String?
public let saturationAvgPercentage: Int?
public let saturationGranularDataPercentage: [RookSaturationGranular]?
public let vo2MaxMlPerMinPerKg: Double?
public let vo2GranularDataMlPerMin: [RookVo2Granular]?
public let stressAtRESTDurationSeconds, stressDurationSeconds, lowStressDurationSeconds, mediumStressDurationSeconds: Int?
public let highStressDurationSeconds: Int?
public let tssGranularData1_500_ScoreNumber: [RookTssGranular]?
public let stressAvgLevelNumber, stressMaxLevelNumber: Int?
public let appleWorkoutIdentifier: String
public let appleDistanceCyclingMeters: Int?
}
public struct RookSpeedGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds, speedMetersPerSecond: Int
}
public struct RookVelocityVectorSpeed: Encodable {
public let speedMetersPerSecond: Int
public let direction: String
}
public struct RookCadenceGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds, cadenceRPM: Int
}
public struct RookTorqueGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds, torqueNewtonMeters: Int
}
public struct RookLapGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds, laps: Int
}
public struct RookPowerGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds, powerWatts: Int
}
public struct RookPositionLatLng: Encodable {
public let lat, lng: Double
}
public struct RookPositionGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds: Int
public let lat, lng: Double
}
public struct RookTssGranular: Encodable {
public let dateTime: Date
public let intervalDurationSeconds, tss1_500_Score: Int
}
⚠️ Deprecated: The below functions are deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Use the functions above instead.
| Method | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
func syncEvents(completion: @escaping () -> Void) | Uploads all the events of previous days that has no been uploaded. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func syncBodyHeartRateEvent(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronized all the body heart rate events from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func syncPhysicalHeartRateEvent(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronized all the physical heart rate events from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func syncBodyOxygenationEvent(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronized all the body oxygenation events from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func syncPhysicalOxygenationEvent(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronized all the physical oxygenation events from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func syncTrainingEvent(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronized all the trainings events from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func syncTemperatureEvents(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronized all the temperature events from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func syncBloodPressureEvents(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronized all the blood pressure events from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func syncBloodGlucoseEvents(date: Date, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Synchronized all the blood glucose events from the given day date. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
We highly advise against retrieving more than 14 days of EPOCH data and 30 days of Daily data for more than one data type. Due to the expected volume of data, the retrieval process will require extensive resources and may affect the user experience.
Data Sources
ROOK SDK includes the class DataSourcesManager, which allows the presentation of a connection page view where users can directly connect other data sources with ROOK. If you prefer to implement your own view, this class also contains a method to retrieve the available data sources for connection.
| Method | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
func getAvailableDataSources(redirectURL: String?, completion: @escaping (Result<[RookDataSource], Error>) -> Void) | Retrieves and array of object representing the available data sources. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
func presentDataSourceView(redirectURL: String?, completion: @escaping (Result<Bool, Error>) -> Void) | Presents a view that contains the available data sources. | ⚠️ Deprecated |
public func getAuthorizedDataSources(completion: @escaping (Result<StatusDataSources, Error>) -> Void) | Returns an object with all the data sources and its connection status. | Available |
public func getAuthorizedSources(completion: @escaping (Result<[DataSourceStatus], Error>) -> Void) | Returns an array with all the data sources available with its connection status | Available |
public func getDataSourceAuthorizer(dataSource: String, redirectUrl: String? = nil, completion: @escaping (Result<DataSourceAuthorizer, Error>) -> Void) | Retrieves the authorization status for a specific data source linked to a given user. - If the user is not authorized, an authorization URL is provided to start the process. - If the user is already authorized, the response will indicate "authorized": true and no authorization URL will be returned. - The redirectUrl parameter can be used to specify where the user should be redirected after completing the authorization. | Available |
Please note that this only represents the user connection status, and not whether the data source is currently active (sending data) or has granted permissions.
For SDK-based data sources (such as Apple Health and Health Connect), this endpoint will return true if the user was created by SDK with the corresponding updateUserId function, means that the user is linked with ROOK via SDK, but not indicates if the user granted permissions or not.
For API-based data sources (such as Fitbit, Garmin, and Withings), true indicates that the user has authorized ROOK to retrieve data through the respective third-party platform.