Health Connect
If you are interested in configure and use Apple Health and Health Connect (Android) we highly recommend to refer to Rook SDK
This SDK enables apps to extract and upload data from Health Connect, with this sdk you will be able to extract and upload data from health connect, if you need check our app demo
Installation
To build a project using the Rook Health Connect in React native you need to use at least react v16 and react native v65. This SDK is only available on Android this means that it won't work with iOS.
The minimum version of android sdk is 26, the target sdk 34 and the kotlin version >= 1.8.10
npm
npm i react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect
yarn
yarn add react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect
Configuration
Add your client uuid in order to be authorized, follow the next example, add at the top level of your tree components the RookConnectProvider, password refers to the secret key.
import { RookSyncGate } from "react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect";
<RookSyncGate
environment="sandbox | production"
clientUUID="YOUR_CLIENT_UUID"
password="YOUR_PASSWORD"
enableLogs={true | false | undefined}
enableBackgroundSync={true | false}
>
<YOUR_COMPONENTS />
</RookSyncGate>;
Then we need to configure the android project. open the android project inside android studio. We need to modify the AndroidManifest.xml file in order to access to the Health connection records.
We need to add inside your activity tag an intent filter to open Health Connect APP and your AndroidManifest.xml file should look like this
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
...
<application
...>
<activity
...>
<intent-filter>
...
</intent-filter>
<!-- For supported versions through Android 13, create an activity to show the rationale
of Health Connect permissions once users click the privacy policy link. -->
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="androidx.health.ACTION_SHOW_PERMISSIONS_RATIONALE" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<!-- For versions starting Android 14, create an activity alias to show the rationale
of Health Connect permissions once users click the privacy policy link. -->
<activity-alias
android:name="ViewPermissionUsageActivity"
android:exported="true"
android:permission="android.permission.START_VIEW_PERMISSION_USAGE"
android:targetActivity=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW_PERMISSION_USAGE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.HEALTH_PERMISSIONS" />
</intent-filter>
</activity-alias>
</application>
</manifest>
Included permissions
This SDK will use the following permissions, there is no need to declare them in your manifest as the rook-sdk already declares them in its own manifest:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACTIVITY_RECOGNITION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.FOREGROUND_SERVICE_HEALTH"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.POST_NOTIFICATIONS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_SLEEP"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_STEPS"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_DISTANCE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_FLOORS_CLIMBED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_ELEVATION_GAINED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_OXYGEN_SATURATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_VO2_MAX"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_TOTAL_CALORIES_BURNED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_ACTIVE_CALORIES_BURNED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_HEART_RATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_RESTING_HEART_RATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_HEART_RATE_VARIABILITY"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_EXERCISE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_SPEED"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_WEIGHT"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_HEIGHT"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_BLOOD_GLUCOSE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_BLOOD_PRESSURE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_HYDRATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_BODY_TEMPERATURE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_RESPIRATORY_RATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_NUTRITION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_MENSTRUATION"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.health.READ_POWER"/>
Google may require you to provide an explanation about the FOREGROUND_SERVICE/FOREGROUND_SERVICE_HEALTH permissions,
these permissions are used by our Automatic Sync and Background Steps features, to extract health data and upload it to ROOK servers. We
recommend you to ask users for permission before enabling these features (Google may also require a video proof of a
screen where a user can turn on/off these features).
Request data access for Android
When you are developing with the Health Connect SDK, data access is unrestricted. To have data access when your app is launched on the Play Store, you must complete the Play Console Health apps declaration. More information can be found here.
You will se a list like below of the permissions your app uses, you will need to provide a description on how your app uses the data of each permission.
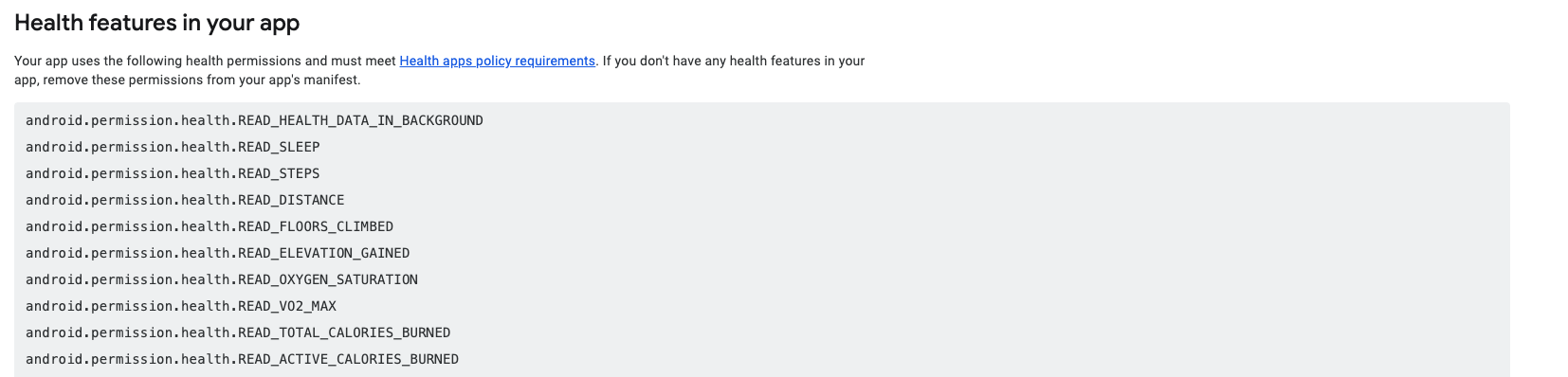
If you don't want access to a particular data type of Health Connect you can remove it.
Obfuscation
If you are using obfuscation consider the following:
In your proguard-rules.pro add the following rule:
-keep class com.google.crypto.** { *; }
In your gradle.properties (Project level) add the following to disable R8 full mode:
android.enableR8.fullMode=false
If you want to enable full mode add the following rules to proguard-rules.pro:
# Keep generic signature of Call, Response (R8 full mode strips signatures from non-kept items).
-keep,allowobfuscation,allowshrinking interface retrofit2.Call
-keep,allowobfuscation,allowshrinking class retrofit2.Response
# With R8 full mode generic signatures are stripped for classes that are not
# kept. Suspend functions are wrapped in continuations where the type argument
# is used.
-keep,allowobfuscation,allowshrinking class kotlin.coroutines.Continuation
# Crypto
-keep class com.google.crypto.** { *; }
Usage
useRookSyncConfiguration
This hook will help you to configure the user ID you want to sync.
The updateUserID should be called as a part of your Log in flow, when your users log out from your app call clearUserID (this is optional as any call to updateUserID will override the previous userID).
import { useRookSyncConfiguration } from "react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect";
const useRookSyncConfiguration = () => {
ready: boolean;
getUserID: () => Promise<string>;
updateUserID: (userID: string) => Promise<boolean>;
clearUserID: () => Promise<boolean>;
syncUserTimeZone: () => Promise<boolean>;
deleteUserFromRook: () => Promise<boolean>;
scheduleYesterdaySync: () => Promise<boolean>;
}
ready: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.getUserID: Return the current user ID.updateUserID: Change the current user ID.clearUserID: Clear the current user ID.syncUserTimeZone: Update the time zone of the user, you should only call this when is strictly necessary.deleteUserFromRook: Delete the user from the Rook services.scheduleYesterdaySync: The functionscheduleYesterdaySyncis an asynchronous function that syncs data of the different summaries and events that Rook has.
Note: If you delete the user from the Rook services you have to create the user again with updateUserID and request permissions.
Any call to updateUserID the userID will override the previous userID and reset the sync status, so if you are using background sync all health data will synchronize again the next time the app is launched.
useRookSyncPermissions
This hook will help you to request permissions to extract data. Before proceeding further, you need to ensure the user’s device is compatible with Health Connect and check if the APK is installed.
import { useRookSyncPermissions } from "react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect";
export type Availability = "INSTALLED" | "NOT_INSTALLED" | "NOT_SUPPORTED";
export type RequestStatusPermissions = "REQUEST_SENT" | "ALREADY_GRANTED";
const useRookSyncPermissions: () => {
ready: boolean;
checkAvailability: () => Promise<Availability>;
openHealthConnectSettings: () => Promise<void>;
checkPermissions: () => Promise<boolean>;
checkHealthConnectPermissionsPartially: () => Promise<boolean>;
shouldRequestAndroidBackgroundPermissions: () => Promise<boolean>;
requestPermissions: () => Promise<RequestStatusPermissions>;
requestAndroidBackgroundPermissions: () => Promise<RequestStatusPermissions>;
hasAndroidBackgroundPermissions: () => Promise<boolean>;
revokeHealthConnectPermissions: () => Promise<boolean>;
};
ready: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.checkAvailability: Check if the health connect service is available.openHealthConnectSettings: Open the health connect settings.checkPermissions: Check if the sdk have the permissions to read data from health connect.checkHealthConnectPermissionsPartially: Check if the sdk have at least one permissions to read data from health connect.shouldRequestAndroidBackgroundPermissions: Check if is necessary to request background permissionsrequestPermissions: Request the permissions for health connect, return two possible valuesREQUEST_SENTmeans that the view requesting permissions was shown orALREADY_GRANTEDmeans that the user is allowed to request permissions.requestAndroidBackgroundPermissions: Request the permissions for enable background sync, return two possible valuesREQUEST_SENTmeans that the alerts requesting permissions was shown orALREADY_GRANTEDmeans that the user is allowed to request permissions.hasAndroidBackgroundPermissions: Check if the app has permissions to access the background servicesrevokeHealthConnectPermissions: Revoke the permissions for granted Health Connect permissions back to false.
You may notice that after calling revokeHealthConnectPermissions the permissions are still granted, however they will be revoked the next
time the app is closed (process stops).
useRookSync
This hook will sync the data according to the options specified
const useRookSync: () => {
sync: (callback: Callback, options?: SyncParams) => void;
syncEvents: (options: SyncEventParams) => Promise<boolean>;
};
sync: This function synchronizes data from yesterday up to 29 days back in the foreground and offers three synchronization options.- empty: If you only pass a callback, the SDK will sync data from the past 29 days.
- options: If you pass a date, summary type, and a callback, the SDK will sync data from the specified date and pillar.
- options.date: If you pass only a date and a callback, the SDK will sync physical, sleep, and body data from the specified date.
syncEvents: This will sync the types of events and date specified
Types
export type SyncParams = {
date: string;
summary?: SyncSummaryType;
};
export type SyncEventParams = {
date: string;
event: SyncEventType;
};
export type SyncSummaryType = "sleep" | "body" | "physical";
export type Callback = (error: Error | null, result: boolean) => void;
type SyncEventType =
| "activity"
| "blood_glucose"
| "blood_pressure"
| "body_metrics"
| "heart_rate"
| "hydration"
| "nutrition"
| "oxygenation"
| "temperature"
| "steps"
| "calories";
export type SyncIOSEventType =
| "activityEvent"
| "heartRate"
| "oxygenation"
| "temperature"
| "bloodPressure"
| "bloodGlucose"
| "bodyMetrics";
useRookSyncSummaries
This hook is deprecated and will be deleted in upcoming versions.
This hook will help you to extract and send data from health connect to Rook servers.
import { useRookSyncSummaries } from "react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect";
const useRookSyncSummaries: () => {
ready: boolean;
syncSleepSummary: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncBodySummary: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncPhysicalSummary: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncPendingSummaries: () => Promise<boolean>;
};
ready: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.syncSleepSummary: Send the summary to rook servers.syncBodySummary: Send the summary to rook servers.syncPhysicalSummary: Send the summary to rook servers.syncPendingSummaries: In case you try to sync a summary and fail, this function help to try to send again.
useRookSyncEvents
This hook is deprecated and will be deleted in upcoming versions.
This hook will help you to extract and send data from health connect to Rook servers.
import { useRookSyncEvents } from "react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect";
export type CaloriesResult = {
basal: number;
active: number;
};
const useRookSyncEvents: () => {
ready: boolean;
syncPhysicalEvents: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncBloodGlucoseEvents: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncBloodPressureEvents: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncBodyMetricsEvents: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncBodyHeartRateEvents: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncPhysicalHeartRateEvents: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncHydrationEvents: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncNutritionEvents: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncBodyOxygenationEvents: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncPhysicalOxygenationEvents: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncTemperatureEvents: (date: string) => Promise<boolean>;
syncTodayCaloriesCount: () => Promise<CaloriesResult>;
syncPendingEvents: () => Promise<boolean>;
};
ready: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.syncPhysicalEvents: Send physical events for the specified date.syncBloodGlucoseEvents: Send blood glucose events for the specified date.syncBloodPressureEvents: Send blood pressure events for the specified date.syncBodyMetricsEvents: Send body metrics events for the specified date.syncBodyHeartRateEvents: Send body heart rate events for the specified date.syncPhysicalHeartRateEvents: Send physical heart rate events for the specified date.syncHydrationEvents: Send hydration rate events for the specified date.syncNutritionEvents: Send nutrition events for the specified date.syncBodyOxygenationEvents: Send body oxygenation events for the specified date.syncPhysicalOxygenationEvents: Send physical oxygenation events for the specified date.syncTemperatureEvents: Send temperature events for the specified date.syncPendingEvents: In case you try to sync an event and fail, this function help to try to send again.
useRookDataSources
This hook enables you to access available ROOK data sources by requesting a JSON object with the information or by displaying a basic view with a set of buttons.
import { useRookDataSources } from "react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect";
export interface DataSource {
name: string;
authorizationURL: string;
imageUrl: string;
description: string;
connected: boolean;
}
type options = {
redirectURL?: string;
};
export type DataSourceType =
| "Garmin"
| "Oura"
| "Polar"
| "Fitbit"
| "Withings"
| "Whoop";
export interface AuthorizedSources {
oura: boolean;
polar: boolean;
whoop: boolean;
fitbit: boolean;
garmin: boolean;
withings: boolean;
google_fit: boolean;
apple_health: boolean;
health_connect: boolean;
android: boolean;
}
const useRookDataSources: () => {
ready: boolean;
getAuthorizedDataSources: () => Promise<AuthorizedSources>;
getAvailableDataSources: (options?: options) => Promise<DataSource[]>;
presentDataSourcesView: (options?: options) => Promise<boolean>;
revokeDataSource: (type: DataSourceType) => Promise<boolean>;
};
ready: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.getAuthorizedDataSources: Provides a list of authorized data sources for the specified user.getAvailableDataSources: @deprecated Return a list of available data sources, with the ability to configure with the options paramgetDataSourceAuthorizer: Retrieves the authorization status for a specific data source linked to a given user. - If the user is not authorized, an authorization URL is provided to start the process. - If the user is already authorized, the response will indicate "authorized": true and no authorization URL will be returned. - The redirect_url parameter can be used to specify where the user should be redirected after completing the authorization.presentDataSourceView: @deprecated Present a default view with the available data sources, with the ability to configure with the options paramrevokeDataSource: Revokes user authorization for the specified data source.
useRookBackgroundSteps
This hook will help you to extract and send data from health connect to Rook servers.
import { useRookBackgroundSteps } from "react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect";
const useRookBackgroundSteps: () => {
ready: boolean;
isStepsAvailable: () => Promise<boolean>;
enableBackgroundAndroidSteps: () => Promise<boolean>;
disableBackgroundAndroidSteps: () => Promise<boolean>;
isBackgroundAndroidStepsActive: () => Promise<boolean>;
syncTodayAndroidStepsCount: () => Promise<string>;
syncTodayHealthConnectStepsCount: () => Promise<string>;
};
ready: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.isStepsAvailable: Verify if the device has this functionality.enableBackgroundAndroidSteps: Start the service for get the steps, and collect all the steps for one hour then the total count will be send to rook servers.disableBackgroundAndroidSteps: Stop the service for get the steps.isBackgroundAndroidStepsActive: Verify if the steps are active.syncTodayAndroidStepsCount: Get the steps from the current day from the android steps system.syncTodayHealthConnectStepsCount: Get the steps from the current day from Health Connect.
Additional notes
In order to include correctly the steps services follow this steps:
- Request Permissions
- Enable background Android steps
- Sync Steps
Customizing the foreground service notification
The steps manager uses a foreground Service which requires a notification to be permanently displayed.
To use your own resources you need to reference them in the AndroidManifest.xml file:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<application>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.STEPS_ICON"
android:resource="@drawable/my_custom_icon"/>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.STEPS_TITLE"
android:resource="@string/my_custom_title"/>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.STEPS_CONTENT"
android:resource="@string/my_custom_content"/>
</application>
</manifest>
Starting on Android 13 (SDK 33) this notification can be dismissed without finishing the service associated with it, then the service will be displayed in the active apps section (This may vary depending on device brand).
useRookBackgroundSync
This hook will help you to start and stop the background sync (only available in android 15+)
const useRookBackgroundSync: () => {
ready: boolean;
scheduleBackgroundSync: () => Promise<boolean>;
cancelBackgroundSync: () => Promise<boolean>;
};
ready: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.scheduleBackgroundSync: Start the service of background sync.cancelBackgroundSync: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.
Sync health data automatically
If you want to delegate the selection and initiation of the appropriate automatic sync method, please request permissions of health connect (useRookSyncPermissions().requestPermissions()), request android permissions (useRookSyncPermissions().requestAndroidBackgroundPermissions()) and set enableBackgroundSync in true.
Sync health data in background (android 15+)
To sync health data in background, use the scheduleBackgroundSync function during your app's initialization phase.
const useRookHealthConnect: () => {
ready: boolean;
scheduleBackgroundSync: () => Promise<boolean>;
cancelBackgroundSync: () => Promise<boolean>;
};
ready: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.scheduleBackgroundSync: Start the service of background sync.cancelBackgroundSync: Indicates when the hook is ready to work.
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
import { View } from "react-native";
import { useRookHealthConnect } from "react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect";
function MyComponent() {
const { scheduleBackgroundSync } = useRookHealthConnect();
useEffect(() => {
tryToStartBackgroundSync();
}, []);
const tryToStartBackgroundSync = async () => {
console.log("Attempting to enable background sync...");
try {
await scheduleBackgroundSync();
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
};
return <View>{/* Your UI components here */}</View>;
}
export default MyComponent;
Sync health data automatically (android 14-)
To automatically sync health data, use the scheduleYesterdaySync function during your app's initialization phase.
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
import { View } from "react-native";
import { useRookSyncConfiguration } from "react-native-rook-sdk-health-connect";
function MyComponent() {
const { scheduleYesterdaySync } = useRookSyncConfiguration();
useEffect(() => {
tryToEnableYesterdaySync();
}, []);
const tryToEnableYesterdaySync = async () => {
console.log("Attempting to enable yesterday sync...");
try {
await scheduleYesterdaySync("oldest");
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error retrieving data from AsyncStorage:", error);
}
};
return <View>{/* Your UI components here */}</View>;
}
export default MyComponent;
RookYesterdaySyncPermissions
scheduleYesterdaySync Requires 2 types of permissions
- Android
- POST_NOTIFICATIONS
- FOREGROUND_SERVICE
- FOREGROUND_SERVICE_HEALTH
- ACTIVITY_RECOGNITION
- Health Connect
- SLEEP
- PHYSICAL
- BODY
To request or check both types of permissions use the you have to request permissions of health connect with useRookSyncPermissions().requestPermissions() in order to access to the health connect data and useRookSyncPermissions().requestAndroidBackgroundPermissions() to have access to the background services
Customizing the foreground service notification
To sync health data automatically a Foreground Service is used, this service requires a notification to be displayed until the synchronization finishes.
To use your own resources you need to reference them in the AndroidManifest.xml file:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<application>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.SYNC_ICON"
android:resource="@drawable/my_custom_icon"/>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.SYNC_TITLE"
android:resource="@string/my_custom_title"/>
<meta-data
android:name="io.tryrook.service.notification.SYNC_CONTENT"
android:resource="@string/my_custom_content"/>
</application>
</manifest>
Starting on Android 13 (SDK 33) this notification can be dismissed without finishing the service associated with it, then the service will be displayed in the active apps section (This may vary depending on device brand).
Launch/Stop conditions
scheduleYesterdaySync won't start or will stop if one the following conditions are meet:
- The device battery is low
- The device storage is low
- The device is not connected to the internet
- The user hasn't granted Android Permissions (POST_NOTIFICATIONS, FOREGROUND_SERVICE, FOREGROUND_SERVICE_HEALTH)
- The device has previously exceeded the Health Connect request quota and the recovery timestamp hasn't been meet
- The user hasn't granted Health Connect Permissions (SLEEP, PHYSICAL, BODY)
- The most recent request exceeded the Health Connect request quota
- The userID hasn't been configured
- There is an error initializing the SDK
Additional information
Health Connect request quota
To maintain optimal system stability and performance, Health Connect imposes rate limits on client connections to the Health Connect API.
It is important for you to understand that every data type in rook-sdk is constructed of multiple health variables like heart rate, steps count, hydration, etc. So when a Sleep Summary is extracted there are multiple calls made to the Health Connect API, and whereas in the last months our efforts have been focused on optimizing and reducing the number of API call required for each data type it's still possible for that limit to be reached, especially while doing multiple extraction in a short amount of time.
Depending on the sync type you chose you must have the following things in mind:
Request quota when syncing data manually
- Extract summaries once daily: Since summaries collect health data from a previous day, there's no need to extract them more than once per day.
- Use what you already have: If you are extracting Physical Events you don’t need to extract Heart Rate Events ( Physical) or Oxygenation Events (Physical) as these are already included in the PhysicalEvent object.
- Only sync the relevant health data for you use case: If you are not interested on individual events and only want to
sync the summary of a specific date, just use the
syncfunctions inuseRookSyncSummaries. - If you already reached the request quota avoid calling any
syncfunction for the next hours so your quota can be recovered.
Request quota when syncing data automatically
scheduleYesterdaySync already takes care of practically all issues and limitations of Health Connect. When the
quota is reached, all pending syncs are canceled, and a recovery timestamp is created. Pending syncs will not resume
until the user re-opens the app after a few hours.
Frequency of syncing with scheduleYesterdaySync
| Health structure | Frequency | Historical range |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep Summary | Each time scheduleYesterdaySync is called | 29 days in the past until yesterday |
| Body Summary | Each time scheduleYesterdaySync is called | 29 days in the past until yesterday |
| Physical Summary | Each time scheduleYesterdaySync is called | 29 days in the past until yesterday |
| Physical Activity | Each time scheduleYesterdaySync is called | 29 days in the past until today |
| Steps | Each time scheduleYesterdaySync is called | Today |
Auto start
After a call to enableBackgroundAndroidSteps if the device is restarted the Foreground service will start after the
user unlocks their device for the first time (This may vary depending on device brand). This behaviour will be stopped
when calling disableBackgroundAndroidSteps.
Considerations
The steps service is designed to always be active but there are certain scenarios where the service could not behave as intended:
- If the user force closes the application from settings, and then restarts their device the service may not be able to restart.
- The steps are scheduled to be uploaded every hour from the time
enableBackgroundAndroidStepswas called, however it's not possible to guarantee the exact execution time as this depends on how the Android System manages the device resources.
Listen for Permissions Notifications
The ROOK SDK allows you to listen for permission notifications, enabling you to respond to changes in permissions, as shown in the following example:
import { getRookModule } from "react-native-rook-sdk";
...
useEffect(() => {
const rookModule = getRookModule();
const eventEmitter = new NativeEventEmitter(rookModule);
// Subscribe to the event
const subscription = eventEmitter.addListener(
"ROOK_NOTIFICATION",
handleRookNotification
);
// Clean up subscription when the component unmounts
return () => {
subscription.remove();
};
}, []);
const handleRookNotification = (notification) => {
const { type, value, message } = notification;
switch (type) {
case "ROOK_BACKGROUND_ANDROID_PERMISSIONS":
console.log(`Background permissions on Android: ${value}`);
break;
case "ROOK_BACKGROUND_ANDROID_PERMISSIONS_DIALOG_DISPLAYED":
console.log(
`Background permissions on Android was displayed: ${value}`
);
break;
case "ROOK_HEALTH_CONNECT_PERMISSIONS":
console.log(`Health Connect permissions: ${value}`);
break;
case "ROOK_HEALTH_CONNECT_PERMISSIONS_PARTIALLY_GRANTED":
console.log(`Health Connect has partially permissions: ${value}`);
break;
case "ROOK_BACKGROUND_ENABLED":
console.log(`Background services enabled: ${value}`);
break;
default:
console.log(`Unknown notification: ${message}`);
}
};
The notification type indicates the following:
ROOK_BACKGROUND_ANDROID_PERMISSIONS: Specifies whether the user has granted Android permissions.ROOK_BACKGROUND_ANDROID_PERMISSIONS_DIALOG_DISPLAYED: Specifies whether the user saw the dialog of permissions.ROOK_HEALTH_CONNECT_PERMISSIONS: Specifies whether the user has granted Health Connect permissions.ROOK_HEALTH_CONNECT_PERMISSIONS_PARTIALLY_GRANTED: Specifies whether the user has granted at least one Health Connect permissions.ROOK_BACKGROUND_ENABLED: Indicates whether background sync was successfully enabled."
Customizing permissions for Health Connect
If you want to reduce the Health Connect permissions used by this SDK you can do it following the manifest merge documentation and the SDK will change the behavior of request/check permissions functions based on the declared permissions:
For example if you remove the READ_MENSTRUATION permission...
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<uses-permission
android:name="android.permission.health.READ_MENSTRUATION"
tools:node="remove"/>
</manifest>
the functions checkHealthConnectPermissions and requestHealthConnectPermissions will check/request all permissions
excluding READ_MENSTRUATION
Note that this process only works for removing Health Connect permissions, adding a permission that is not included in the default list will do nothing.
Health Connect permissions are declared with the syntax: android.permission.health.READ.., to see the current Health Connect permissions go to you AndroidManifest and select the merged manifest tab.